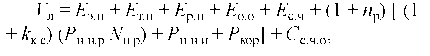НАУКА
The article highlights purposes, tasks, functions and challenges associated with the implementation of self-regulation, Russian and overseas practices of operation of self-regulated organizations in the sphere of receivership and in other economic sectors, as well as initial results of the realization of a concept of improving the self-regulation mechanisms. The article describes the rationale for directions and methods of improving the self-regulation institute
The Article is dedicated to research of the ways to achieve Russia’s strategic goals in the sphere of industrial development under the conditions when import substitution has become one of the main governmental policy trends over the recent years. It is shown that the industrial policy should be underpinned by the project management in order to ensure sustainable development of the key sector of the national economy. Systematized are priority methods of long-term support of industrial enterprises aimed at enhancing the competitiveness of domestic products.
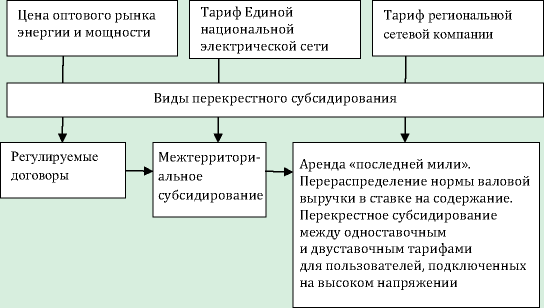
The paper is devoted to economic effects of decrease in volumes of cross subsidizing for participants of the market of electric energy are considered, and also methodological approaches to modeling of a stage-by-stage decrease of volumes of cross subsidizing in economy are developed. The methodology of the system of national accounts (SNA) – symmetric tables “expenses – release” and intersectoral balance “a product – a product” calculated on release of the final product of 22 industries – was used to model the influence of economic and social effects due to cross subsidies elimination. The comparative analysis of one-stage and gradual options to cross subsidies elimination was carried out. One-stage elimination of cross subsidizing showed more the worst results on economic indicators of participants of a power market, than at its stage-by-stage decrease.
Modeling of stage-by-stage decrease in cross subsidizing is aimed at determination of the greatest possible growth rate of tariffs for the electric power for the population. The indicator of the minimum value of economic damage to branches of the economy, calculated as a difference of a balanced gain (departure) of a gross value added in the range of a threshold interval of increase in expenses of house farms on the purchased electric power in the general structure of expenses is used as criterion of an optimality of growth rate of tariffs for the electric power. The macroeconomic model of formation, use and reproduction of a branch value added is used for creation of model. The analysis of impact of change of tariffs for the electric power for the population is carried out with a step to 1% to the level providing full reduction of cross subsidizing. Optimum speed of a gain of tariffs for regions with the maximum rate of a tariff for the electric power (Moscow region) and the minimum rate (Orenburg region) is calculated.
An approach to finding reasonable prices developmental works on creation of aviation equipment for defense purposes is based on the method of successive approximations.
The content of this method, its advantages and the reasons limiting its use is disclosed. Practical steps for its implementation in enterprises-performers of ROC of aviation technology for defense purposes are proposed.
Significant institutional weaknesses of the formation of the management structure of an industry cluster are revealed, the possibility of engineering new structures of governance based on the principles of innovative management is identified. Feature of industrial clusters is the need and necessity of innovation that permeates all structures of the cluster management and all the processes of cluster management and, in turn, creates the preconditions for the formation of business entities the ability to successfully overcome a crisis situation. The purpose of the work is to develop the improved construction of innovational sectorial clustering with the use of effective centralized system of management of cluster business processes, based on diffusion of innovational technologies and their production embodiment. A typical structure of sectorial cluster management does not allow determining goals, tasks, tools, and mechanisms of innovational development of sectorial cluster’s enterprises. Drawbacks of the typical structure of sectorial cluster management are as follows: lack of representation of the scheme of cooperation between cluster members and external environment, format of development of interrelations between cluster’s elements in the sphere of information exchange, movement of material flows and financial resources, lack of formed areas of responsibility and matrices of competences of cluster members in various scenarios of development of external environment.
The “structural imbalance” in the system of management of sectorial cluster is determined, which consists in elaboration of production and functional structure and “fuzziness” of responsibility for cluster activities efficiency. The use of the improved innovational construction of sectorial cluster management will eliminate structural imbalance in the process of management of sectorial clusters and increase effectiveness of their activities under the conditions of turbulent development of external environment.
There are shown actual issues of applying modern information technologies to provide effective anti-crisis management. There has been analyzed aspects of using Internet resources to assess the counterparty’s (debtor’s) insolvency (bankruptcy) risk.
Today the bankruptcy institution develops dynamically under the influence of various factors. This is required the formation of the universal goals of the bankruptcy institution with considering of features of the current socio-economic development. On the other hand, the transformation purposes of the bankruptcy institution towards rehabilitation focus is not always accompanied by an increase of efficiency of bankruptcy procedures, that confirms by the statistics data in the Russia. Thereby author investigated the issues of determining the universal target installation of bankruptcy institution, as well as an analysis of the bankruptcy models, which confirmed the effectiveness of the bankruptcy models in which decisions on rehabilitation or liquidation of the debtor is based on value criteria. In order to enhance the rehabilitation capacity of the bankruptcy institution in Russia on the basis of a systematic approach author proposed changes in the concept of the impact of the bankruptcy procedures, measures to improve the efficiency of bankruptcy procedures, and explore the essence of the process of restoring the debtor's solvency. It is proved that the purpose of rehabilitation of bankruptcy procedures should be the preservation of the debtor's business with the new owner of more efficient, taking into account interests of society as a whole.
The purpose of the study is determined by the need for further development and improvement of methodology of economic diagnostics. The study of theoretical issues and practical implementation of diagnostic studies and crisis management showed that the methodological basis of economic diagnostics needs work and updating, can extend practical approaches to research. Research complement and deepen the complex scientific and theoretical developments in the methodology of economic substantiation of diagnosis. The author presents a methodological approach to the classification of types of diagnostic studies on various grounds. The main emphasis in the developed classification of types is made on a thorough and complete rationale for each attribute, put with the basis of the classification of economic diagnostics, and describe the direction of the diagnostic study.
The article represents main terms of motivation environment concept, elaborated by the author, as an instrument for personnel involvement growth in a company’s innovation process. Analysis of motivation environment components in Russian high-tech innovation-oriented companies “AO «NPO “Krypten»” and “OOO «Verilion»” is held, and problem aspects, which prevent to the companies' effective activity are defined. Practical instruments and recommendations for their solution are offered. Positive influence of motivation environment in a process of commercial organisations' strategic development is proved.
ISSN 2618-9984 (Online)