Статьи
The article is devoted to the analysis of research in the field of typology and classification of innovations. We consider three types of classification the second innovation: the classification by type of innovation and application; classification of innovations by degree of novelty and level of change; rating by innovation. The article proposes a fourth approach to classifying innovations as possible to manage them. The signs of controllability for classification are highlighted:
• adaptability (degree to which the innovation can be changed to satisfy requirements),
• applicability (level of use of innovation in multiple settings),
• relatedness (connected with the main business of the innovator),
• architecture (shows how much innovation should be built into the system for application (or can be used independently without rebuilding the entire system as a whole),
• autonomy (to be able to use innovation regardless of other novelties),
• centeredness (reflects the level to which innovations can influence operations that are critical to organizational effectiveness),
• sociability (the degree to which individual aspects of innovation nations can be transferred to others to form a positive attitude towards its adoption),
• compatibility (the degree to which innovation is perceived as consistent with existing values, experience and the needs of potential followers).
The types and classifications of product, technological (process), marketing, organizational and managerial innovations are examined. The so-called simulative innovations are separately considered. The analysis of the innovation activity of industrial companies made it possible to single out another new type – “value” innovations, which is the main theoretical contribution of this work.
The digital transition in the electric power industry is a promising goal for the development of the industry. In recent years, a wide range of technologies has been introduced into various types of activities of energy companies, including significant attention being paid to technologies that implement demand-side management, transferring consumers from the passive category to active consumers, and also opening up new opportunities in energy management. Non-intrusive load monitoring technology is of significant interest for both electricity suppliers and consumers in the USA and EEC countries, however, a Russian-language study is being carried out for the first time.
The purpose of the study is to consider the concept of non-intrusive load monitoring, to formulate and systematize the effects for electric power industry entities and consumers of electricity from the introduction of technology.
A review of literary sources is carried out, the most cited articles on this topic are analyzed. To calculate the propagation rate of non-intrusive load monitoring, the Bass innovation diffusion model was used. The model allows to perform an assessment based on data on similar products and has established itself as sufficiently effective for predicting the distribution of durable goods, the actual information for which has not yet been collected.
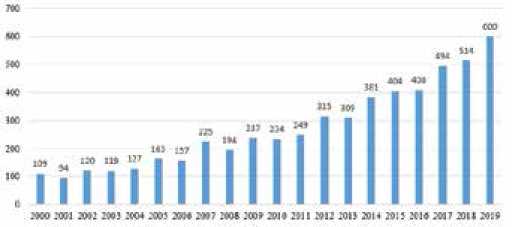
For the first time, a classification of effects arising from the introduction of technology is proposed. The paper obtained a range of effects for households, energy companies, business and government. The calculation of the technology distribution rate showed that without the use of technological corridors and the systematic introduction by energy companies, the peak of adoption can be reached by 8 years from the start of implementation.
Non-intrusive load monitoring allows you to get a wide range of data in order to further optimize energy consumption, increase the efficiency of enterprises, monitor the operation of equipment. There are great opportunities in the commercialization of collected data.
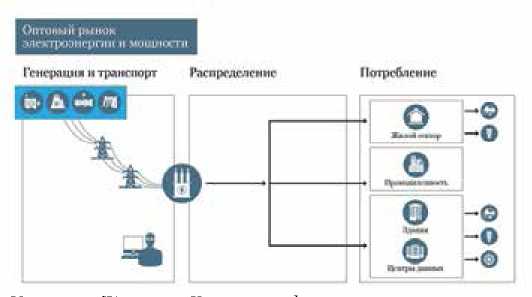
Transition to digital technologies in management of power industry at all levels – an inevitable consequence of the technical progress which has generated opportunities for diversification, decarbonization and decentralization. Thus it is necessary to recognize that digitalization in power industry is NOT automation, and first of all creation of new business models, services and the markets with a support on possibility of digital economy. In this article questions of transformation of architecture of power industry, and also the main restrictions are considered: absence in regulatory base of new opportunities for consumers; general system inefficiency; impossibility “to legalize” appearance of new subjects (active consumers and prosumers, operators of micropower supply systems and aggregators of the distributed power objects, various service organizations), and also to deregulate the relations between them, to standardize interaction interfaces with EEC, to transform the energy markets.
In article it is offered for transition to new digital power to make corresponding changes to the legislation: to enter new type of participants of the market (the active consumer, an active power complex), operated intellectual connection carrying out the standard with the electrical power system, completely responsible for management of the power supply and thus having the minimum regulatory restrictions on organizational model of the work; to improve rules of functioning of trade systems for creation of the markets of the distributed power providing an effective exchange of goods and services between traditional participants of the markets and participants of new type; to enter possibility of application of technologies of the coordinated management of the distributed sources and consumers of energy, systems of storage of energy, means of regulation of loading (“aggregators”) for the purpose of increase of efficiency of their use and participation in the electric power and power markets, including rendering system services and performance of other functions in these markets (the pilot project of such system is realized under the leadership of the author of the present article by subsidiary PAO “Lukoil” “Energy and gas of Romania”); to increase technological and economic flexibility of conditions on reliability and quality of power supply, creation of possibility of a choice by the consumer of conditions of power supply necessary for him and the account them in cost; to enter the accounting of the opportunities given by “new” decisions, at an assessment, formation and implementation of investment programs of the adjustable companies (including introduction of a technique of an assessment of investment projects at possession cost on all life cycle of the decision); to replace cross subsidizing of the population by industrial consumers with mechanisms of address social support and / or with system of restriction of volumes of consumption on reduced rates (“соцнорма”); to refuse further deployment of system of subsidizing of power supply of one regions at the expense of consumers of other regions (as it leads to growth of inefficient power consumption in the subsidized regions, not provided with available generation and infrastructure); to change norms of technical regulation, norms of design on the basis of new technologies; to make changes to programs of development of the infrastructure organizations of power industry taking into account trends of diversification, decentralization, decarbonization and a digitalization; to provide possibility of stimulation, including tariff, implementation of regional programs (pilot and regular), aimed at the complex development of power industry on the basis of new approaches, technologies and the practician, and also the hi-tech companies of small and medium business providing development.
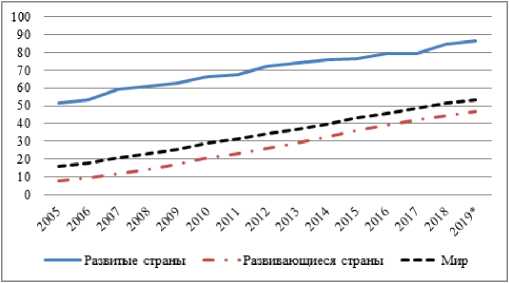
The digital transformation of the economy leads to dramatic changes in business and society and requires the reconfiguration of all socio-economic institutions. Such radical changes include economic science and management, challenging the traditional economic laws and management tools that were formed in the “digital era”. The purpose of the study is to identify the key challenges of the digital transformation of the economy for economic science, management and business, as well as the main directions of development of crisis management of companies in the era of the digital economy.
The study identified the main factors of digital transformation of the economy that affect the methods and conditions of doing business, and the challenges of digitalization for business. The necessity of developing a new crisis toolkit for companies of the “digital” and “non-digital” eras is substantiated, for which a comparative analysis of the characteristics of such companies and key indicators of their financial and economic status is carried out. In addition author defined several economic paradoxes that the author called the “scissor effect” (a gap in the dynamics of the capitalization of digital and non-digital companies) and the “paradox of profitability” (growth in the capitalization of digital companies against the backdrop of chronic loss-making activities).
Author used various methods of scientific research: deduction and induction when conducting an empirical analysis of the activities of digital and non-digital companies, analytical methods and historical analysis.
The results of the study will contribute to the development of the theory of management and crisis management in the era of the digital economy, and also will determine the future directions of theoretical and practical development of these scientific disciplines.
The article analyzes the international Supervisory experience of the European Union in terms of monitoring the implementation of short sales. The analysis was carried out in order to determine further key directions of development of the Russian market of margin lending. In addition, the article also considers the current Russian legislation in terms of supervision of unsecured transactions, regulated by the Decree of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, which entered into force on July 1, 2019. The obtained results of the analysis allowed to make a comparative characteristic of the regulation of short sales in the European and Russian jurisdictions, as well as to make a forecast regarding the hypothetical transformations of the current Russian legislation.
The analysis of the European experience in part of control of implementation of the short sales established by SSR to disclosure of information on short positions, to restrictions on short sales, to powers and ESMA obligations, etc., allows to come to conclusion that regulation in the Russian jurisdiction can be expanded not only due to complication of a procedure for granting of a marginal loan by inclusion in a portfolio of the client of difficult nonlinear tools, but also due to establishment of requirements for disclosure of information on the high-concentrated short positions and establishment of thus constantly reconsidered threshold size. In article the assumption that the designated directions of development of regulation of short sales regarding expansion of powers of the regulator also will increase transparency of intermediary activity and the financial market is made, having provided thus reliable protection of interests of clients of financial intermediaries.
The author considers features of the economic nature of activity of the shareholder in corporate governance and in the control over management. The author offers the standard of the diligent shareholder and the standard of the diligent management as necessary condition for rapprochement of long-term financial interests. Reasonable and diligent realization of the corporate rights, display of interest to company activity will allow the shareholder to receive the information on the concluded transactions. The information on transactions will allow to protect the broken rights in the terms established by the law. The reasonable management within the limits of standard administrative practice should make the maximum efforts for achievement of firm wealth maximization and also consider factors which to a greater or lesser extent influence firm wealth maximization and can be considered as the independent purposes at a certain stage of activity of the company. The company it is necessary to implement the motivation program for rapprochement of long-term financial interests of the shareholder and the management. The motivation program means reception of property benefit from increase in a stock value (share) of the company which possibility of reception is the circumstance stimulating management to act in interests of the company. According to the best practice of corporate governance level of the compensation paid to management, should be sufficient for attraction, motivation and deduction of the persons possessing necessary for company professional skills and qualification, and the compensation system should provide rapprochement of financial interests of directors with long-term financial interests of shareholders. The clause is interdisciplinary, covering elements of corporate governance which are a part of the corporate finance as sciences, and also, the corporate right.
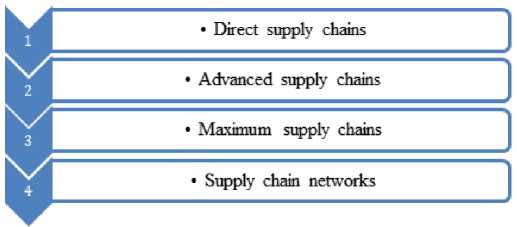
Attention growth to management of chains of deliveries has caused search of new ways of improvement of logistic processes. At the same time the question of a role of the theory of stakeholders in formation and maintenance of chains of deliveries was staticized. The main attention of the concept of interested parties of rather logistic processes has concentrated on the main points of decision-making in a choice of routes for transportation of freights. In article the methodical approach developed by authors to the analysis of extent of influence of interests of stakeholders in management of chains of deliveries within digital transformation of logistics is considered. For a choice of optimum option of transportation of the freights, most realizing the transport capacity of Russia, authors have taken as a basis A. Garrison's fundamental approach, allowing to develop methodical approach to an assessment of interests of stakeholders of the international logistic knot of the country. The circle of the stakeholders (interested parties) involved in process of decision-making on a choice of an optimum route at implementation of transportation of freights is created. The main transnational corridors of transportation of goods from the People's Republic of China in the European Union and criteria by which it is possible to carry out their assessment for a choice of the most acceptable are defined. Methodical approach to an assessment of degree of compliance of routes to certain criteria according to interests of stakeholders is developed. Comparison of criteria among themselves, and also an assessment of their influence in each option of transportation have shown as far as interests of stakeholders of chains of deliveries differ. The hierarchy of the importance of each criterion for the described routes of transportation taking into account interests of stakeholders of chains of deliveries is created. The conclusion is drawn that the main factor in transportation of goods when using capacities of Russia is time. This criterion plays a significant role at a route choice, however at the high cost and insufficient reliability such route will concede in most cases to competitors. Proceeding from it, attraction of opportunities and advantages which can provide other options, becomes quite expedient. Thus, harmonization of the relations of stakeholders is reduced uniting their interests of rather allocated options of transportations on development of Russia as the international logistic knot and to show, what economic benefits they can receive from this interaction.
Today flexibility is becoming one of the most important capability in business, because the product life cycle is reduced, the external environment of organizations is constantly changing, technologies are improving every day. In such circumstances, companies cannot afford to develop technologies exclusively in R&D departments in their companies; this is unproductive, inefficient and expensive. Companies “opened” their innovation processes to improve their innovation potential. The relevance of this work is due to the great interest of both the scientific community and practitioners in the instruments and strategies needed for successful adoption of the theory of open innovation.
The objective of this study is to provide a comprehensive review of the progress on open innovation literature reflecting the most essential topics to be covered in future research. This survey study makes a significant contribution to the research of the open innovation theory. The article offers a detailed overview of the various views and studies related to this topic. The evolution in the field of research of open innovation theory is presented here. The article is structured as follows: the link between open innovation and other theories in management, the adoption of open innovation paradigm in different industries, the influence of adopting the open innovation theory on the business, criticism of the open innovation theory, researches studying open innovation theory conducted in Russia, classification of frameworks in the open innovation theory. This article describes the state of open innovation at the intersection of research, practice, and policy.
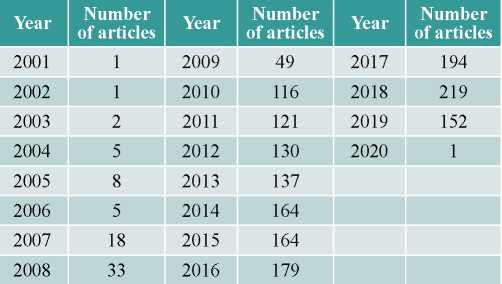
In addition, this work focuses on the most cited publications of the most cited scientists, as well as on the work of the last two to three years.We combinebibliographic analysis of all papers on the topic published in Scopus database witha systematic content analysis of the field to develop a deeper understanding of earlier work.
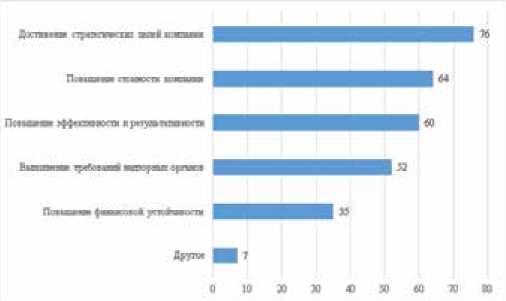
The article analyzes the practice of implementing risk management in Russian industrial companies. The study conducted a survey of 96 industrial companies in various industries in order to identify the features of implementing a risk management system in Russian industrial organizations. The main goals of implementing risk management systems in industrial companies, the features of organizational risk management structures, the amount of costs for maintaining risk management systems, risk assessment methods, the activities of industrial organizations that integrate risk management processes, and the level of automation of risk management systems were identified.
The method of assessing the level of maturity of risk management is proposed: absent, managed, quantitatively managed, optimized and advanced levels.
Using cluster analysis, groups of Russian industrial companies in various industries were identified by the level of process maturity of the risk management system. The most developed in the field of risk management systems are companies in the mining industry, mechanical engineering, as well as those engaged in the production of consumer goods. Companies with the least developed level of risk management include companies in the furniture, pulp and paper, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical industries, as well as those that produce building materials.
On the basis of the survey identified the main barriers introducing a comprehensive system of risk management of industrial companies.
The described research areas will help to increase the effectiveness of the risk management system, which will help to increase the strategic stability of the company.
ISSN 2618-9984 (Online)