Статьи
Digital societies come with a design paradox: On the one hand, technologies, such as Internet of Things, pervasive and ubiquitous systems, allow a distributed local intelligence in interconnected devices of our everyday life such as smart phones, smart thermostats, self-driving cars, etc. On the other hand, Big Data collection and storage is managed in a highly centralized fashion, resulting in privacy-intrusion, surveillance actions, discriminatory and segregation social phenomena. What is the difference between a distributed and a decentralized system design? How “decentralized” is the processing of our data nowadays? Does centralized design undermine autonomy? Can the level of decentralization in the implemented technologies influence ethical and social dimensions, such as social justice? Can decentralization convey sustainability? Are there parallelisms between the decentralization of digital technology and the decentralization of urban development?
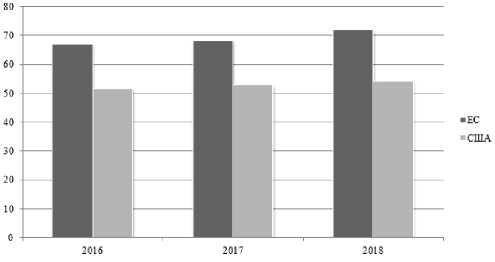
At the international level, the problem of the need to increase the contribution of renewable energy sources to domestic electricity demand is highly relevant. Since the production of renewable energy sources is quite expensive, many countries are developing various state and market incentives for investment in such energy sources. One such incentive is renewable energy certificates. The role of these certificates in the development of global renewable energy markets is invaluable. They not only help businesses achieve their goals in the field of renewable energy, but also reduce consumer payments for other renewable energy development programs. This article analyzes the current trends in the use of renewable energy certificates in the world and identifies the prospects for their use in the Russian Federation. In addition, the author of the article studied the issue of cost-effectiveness of renewable certificates. In order to assess the positive economic impact of the application of the certification system, calculations have been made to reduce the financial burden on participants in the Wholesale Electricity and Power Market by taking into account the funds received from the sale of these certificates to reduce payments by market participants to generators based on renewable sources under the program of agreements on the provision of capacity for generating objects operating on the basis of renewable energy sources, from the date of the start of supply of electric energy and of the last planned facility until the date of the last payment under the power capacity agreement. In addition, the author of the article studied the need for renewable energy certificates not only to obtain reliable data on the use of renewable energy sources, but also to create efficient electricity markets using renewable energy sources around the world.
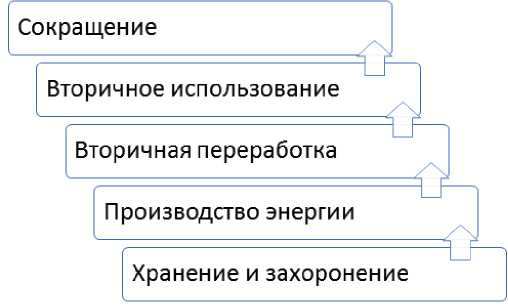
The article analyzes the current state and world experience of the waste management sphere, identifies the reasons for incinerators development, identifies and classifies the main mechanisms for returning investments in their construction. The necessity of building incineration plants in Russia is demonstrated.
Has been given a critical analysis of the plan of new waste incineration plants development in Russia. Has been made an inference about their environmental safety and the possibility of equating this type of generation theoretically and legislatively.to renewable.
A qualitative and quantitative analysis of the planned method of return on investment was carried out. It was established that the use of power supply agreements as a mechanism for the return on investment is impractical. Rational methods of return on investment were identified: the mechanism of free bilateral agreements, inclusion in the structure of regime facilities and combining the selling of electricity in the balancing market and the day-ahead market with the selling of utilization services. The combination method turned out to be optimal, recommendations for its usage are given.
Thus, the article developed recommendations on the usage of mechanisms for the return on investment in the incinerators development in Russia by selling electricity and power.
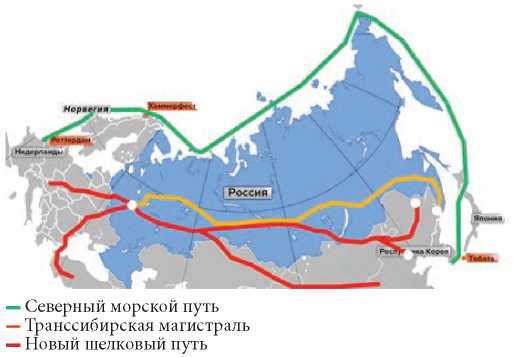
The article reveals the concept of a logistics unit, logistics and digital hubs. It is considering the possibility of combining the Northern Sea and New Silk Way sections into a single system on the territory of the Russian Federation. The authors investigated the ways of digitalization of the logistics block of the NSR – NSW with the subsequent creation of a virtual space for the control and redistribution of trade throughout the Russian Federation. The concept of a digitalized logistics block is considered from the point of view of a potentially beneficial project for Russia to collect statistical data and accelerate international transport by instantly redistributing routes.
The article gives an overview on existing the incentives and barriers of innovation activity that the company forces with when it enters foreign markets. The main incentives are: communication with suppliers, foreign partners, and customers; economies of scale; financing; the nature of the demand and the external economic conditions. Barriers are: competition; risks and costs associated with entering foreign markets; lack of financing and information, qualified personnel, government support; long payback period; technological lag and instability of the economic environment. Сountry analysis showed that the government is more profitable when it develops its own innovations rather than imports them. In countries with developed innovative strategy (Great Britain, Germany, USA, France, Japan, and Republic of Korea), the share of innovative industries in gross output and in export volume is significantly higher than in countries with a development model. These countries have created an innovative culture in which all participants interact in the process of increasing the country's competitive advantage.
According to an econometric analysis conducted in the study, it was concluded that the Russian export indicator depends on the internal scientific developments, the costs for implementing high-tech innovations and the number of registered patents, and in 2020 these indicators will develop with the same trend.In the article, the author attempts to identify the scalability factors of Russian EdTech startups, as well as offer recommendations for building a scalable business model. As a result, the author identified five groups of factors affecting the business model scalability and, somewhat, the success of an EdTech startup. It is especially important that this groups of factors correspond to the most important business model elements of an early-stage startup: the market (or “Customer segments”), the product (or “Value Proposition”), customer relations, distribution, as well as resources regarding the team and investments. Such a complex set of factors interconnected with the main elements of the business model can become a tool for making more effective management decisions, reducing entrepreneurial risks, and increasing the success possibility of an educational project. It was also discovered that copying the leader’s business model is not a relevant strategy for an educational startup and the subscription model does not affect success. On the contrary, the orientation to the global market, the key market trends exploitation, and high-quality distribution and promotion affect scalability and success.
The article is devoted to the optimization of the processes of organization and management of international megaprojects based on the formation of a risk management system.
Currently, the implementation efficiency of megaprojects remains low due to the emergence of many risks at various stages of project implementation.
In this connection, it is proposed to form an integrated risk management system, which implies a three-stage structure for introducing the 6 element risk management system into the project life cycle, into the main project management processes.
This article substantiates the need to form a risk management system in three stages in accordance with the key elements of a risk management system: (1) Planning – the block «Objectives and environment of the project»; (2) Approval of the project – the blocks «Identification», «Classification», «Assessment of risks and risk tolerance», «Risk management plan»; (3) Monitoring and control – the block «Control and monitoring of risks».
Thus, the proposed integrated risk management system provides: continuity of the risk management process based on the audit of the RMS; the ability to adjust RMS at the stage of forecasting a risk event; possibility of scenario modeling for forecasting risk reduction potential; risk management program, formed by current risks in order to increase the attractiveness of the mega-project for the investor.
It is also proposed to introduce an audit of risk management processes and procedures based on an adapted methodology for the following components of the risk management system: defining events and setting goals; the internal environment of the organization; organization risk assessment; risk control tools; responding to risks; communications and information; risk monitoring.
This technique allows you to take into account risks not only at the stage of project development, but also during its implementation, which ensures its feasibility, as well as an audit algorithm for risk management systems of a megaproject is developed and recommendations for improving the RMS through this tool are proposed.
ISSN 2618-9984 (Online)