Scroll to:
FORMATION OF A STRATEGY AND MECHANISM OF INTERACTION BETWEEN PARTICIPANTS OF DIGITAL PLATFORMS
https://doi.org/10.17747/2618-947X-2022-3-255-266
Abstract
The article reviewed the literature in the framework of the study of digital platforms. The main types of digital platforms were considered: instrumental, infrastructural and applied. Within the framework of three types of digital platforms, the features of the of interaction mechanism between their participants are considered.
A study was also conducted in terms of determining the levels of interaction between participants of digital platforms within the framework of social, managerial, economic and technological activities. It was revealed that, in general, within the framework of digital platforms, their participants are characterized by a high level of relationships.
At the same time, the article conducted a study to determine the role of each participant in the development of their interaction within digital platforms of instrumental, infrastructural and applied types. It is revealed that the development of relationships between participants of digital platforms is influenced by the integration of all participants providing a synergistic effect.
Keywords
For citations:
Kuznetsova M.O. FORMATION OF A STRATEGY AND MECHANISM OF INTERACTION BETWEEN PARTICIPANTS OF DIGITAL PLATFORMS. Strategic decisions and risk management. 2022;13(3):255-266. https://doi.org/10.17747/2618-947X-2022-3-255-266
Введение
In the modern world, there is an active change in the architecture of markets, a transition to platform technologies is underway, which is the main trend of the fourth industrial revolution. The main characteristic criteria of digital platforms are [Digital platforms.., 2018; Rohn et al., 2021]:
– algorithmisation of interaction between participants on digital platforms;
– mutually beneficial relations of all participants on digital platforms;
– a significant number of participants operating on digital platforms;
– ensuring a unified information environment for the effective functioning of digital platforms;
– reduction of transaction costs in the implementation of the interaction of various participants on digital platforms.
An important role in shaping the effective functioning of digital platforms is played by the participants, and the relationships built between them within a digital platform. This article discusses the mechanism of interaction between participants on digital platforms within three types of digital platforms.
-
Prerequisites for the formation of a mechanism for interaction between the company and partners
Let us consider the existing relationship management strategies in industrial companies.
There are several groups of strategies for managing a company's relationship with partners [Kushch, Smirnova, 2007]:
- supplier relationship management strategies;
- customer relationship management strategies;
- integrated models of relationship management between partner companies.
Groups of supplier relationship management strategies are presented in detail in Table 1.
At the same time, customer relationship management strategies also have their own classification (Table 2).
There are also integrated models for managing relationships between partner companies (Table 3).
Next, the main participants and their relationships within various types of digital platforms will be considered.
-
Main types of digital platforms
PJSC Rostelecom in the report gives the following definition of a digital platform: a digital platform is a system of algorithmic mutually beneficial relations between a significant number of independent participants in an industry (or field of activity) carried out in a single information environment, leading to a reduction in transaction costs through the use of digital technology package for working with data and changing the division of labor system [Digital Platforms.., 2018].
There are several types of digital platforms, which are presented in Table 4.
It should be noted that instrumental digital platforms make it possible to reduce the cost of developing software and hardware-software solutions. Infrastructural and applied digital platforms are aimed at reducing transaction costs [Digital platforms.., 2018].
-
The mechanism of interaction between the participants of the instrumental digital platform
The work of instrumental digital platforms is based on the interaction of three groups of participants: platform developers, solution developers and users. Fig. 1 and Table 5 show the features of the mechanism of interaction between the participants of the instrumental digital platform.
It should be noted that all participants of the instrumental digital platform play significant roles in the formation of effective relationships and ensuring the functioning of the digital platform. The mechanism of the instrumental digital platform is built on the synergistic principle of interaction between participants to form software solutions for users of the instrumental digital platform [Kushch, Smirnova, 2007; Galagan, 2019; Digital marketplace.., 2022; Ratten, 2022; Xie et al., 2022].
-
Mechanism of interaction between participants of the infrastructure digital platform
The functioning of infrastructure digital platforms is based on the interaction of five groups of participants: platform developers, platform operators, information providers, users of IT services, developers of IT services. Fig. 2 and Table 6 show the features of the interaction mechanism for participants in the infrastructure digital platform.
It should be noted that in the infrastructure digital platform, the functions and roles of participants are similar to the functions and roles of participants in the instrumental type of digital platforms: for example, developers of a digital platform must ensure a unified technological system of the digital platform and the effective functioning of the platform. However, the infrastructure digital platform, unlike the instrumental platform, provides consumers in various sectors of the economy with solutions to automate their activities based on end-to-end digital technologies for working with data and access to data sources that are implemented in the ecosystem infrastructure. At the same time, infrastructural digital platforms make it possible to provide services for legal entities in various sectors of the economy [Digital platforms.., 2018; Galagan, 2019; Wagner et al., 2021; Choosing a Transformational Solution, 2022; Liu et al., 2022; Approaches to the definition.., b.g.].
-
Mechanism of interaction between participants of the applied digital platform
The work of applied digital platforms is based on the interaction of four groups of participants: suppliers of goods and services, platform operator, consumers, regulators. Features of the interaction mechanism of applied digital platforms are shown in Fig. 3 and in Table 7.
The mechanism of applied digital platforms allows for the exchange of values between a significant number of sellers and buyers. The ability to exchange value is the main distinguishing feature of applied digital platforms from others [Stecken et al., 2019; Cozzolino et al., 2021; Approaches to the definition.., no date.].
Thus, the proposed mechanisms for building digital platforms will allow to:
- ensure integration of services, technologies and participants of digital platforms;
- reduce transaction costs and increase competitiveness;
- ensure the efficiency of the digital platform.
-
The main characteristics of the interaction mechanism between participants on digital platforms
As part of this work, a study was conducted to identify various aspects in the relationship between participants on digital platforms. The study was conducted on the basis of the methodology presented in the scientific report by S. Kushch and M. Smirnova "The mechanism for coordinating the processes of managing the company's relationship with partners" [Kushch, Smirnova, 2007]. In their study, they considered the most important characteristics of the mechanism of dual relationships "consumer - key supplier" in the following areas of relationship analysis: social, economic, managerial and technological. The author of this work considered the same aspects but within the framework of the interaction mechanism between participants on digital platforms.
The study was conducted in two stages: conducting a survey of experts to determine the level of relationship between participants on digital platforms; processing of received information. Let us consider each stage of the study in more detail.
At the first stage of the study, a survey of 91 industrial companies was conducted. The main criterion for selecting companies was their consent to participate in a study to determine the level of relationships between participants in digital platforms. Table 8 provides a description of a sample of industrial companies.
The experts were asked to assess the level of the relationship between the participants of digital platforms by determining the level of each of the four areas (Table 9). It is important to note that if the aspects of the line are low, this does not mean that the level of relationships between participants in digital platforms is low. For example, in order to state that the level of relations between participants on digital platforms within the framework of an economic line is high, it is necessary to have a low level of aspects of this line (that is, a low level of costs and investments).
At the second stage of the study, the information obtained during the survey of experts was processed; the results of the study are presented in Fig. 4.
Social direction. As part of the functioning of digital platforms, most experts note a fairly high level of relationships according to the social direction. According to experts, such social aspects as cooperation, flexibility, willingness to adapt, trust, conflict management are at a high level. The use of power is noted as a low-level social aspect, since the functioning of digital platforms makes it possible to increase the transparency of work and improve monitoring of relationships and communications between participants on a digital platform, which makes it possible to ensure work according to uniform rules and standards for all participants [Kushch, Smirnova, 2007; Silva et al., 2021].
Management direction. According to the interviewed experts, digital platforms allow to build a high level of relationships in the management area. This is confirmed by the fact that the planning of relationships and communications, the distribution of responsibility between all participants on the digital platform, the exchange of information, and the monitoring of relationships are built at a high level due to the introduction of a digital platform at an industrial enterprise [Kushch, Smirnova, 2007; Silva et al., 2021].
Economic direction. The introduction of digital platforms in industrial enterprises can significantly reduce costs, which is confirmed by the results of the survey. The costs of maintaining relationships, the costs of terminating relationships and investments are reduced due to the operation of the digital platform, which confirms the high level of relationships in the field of economic direction [Kushch, Smirnova, 2007; Silva et al., 2021].
Technological direction. The relationship of participants within the technological aspect is also at a high level due to the introduction of digital platforms; it is confirmed by experts. Adaptation of products, technologies and business processes is recognised as being at a high level [Kushch, Smirnova, 2007; Silva et al., 2021].
The article also conducted a study to determine the role of each participant in the development of their interaction within three types of digital platforms. The study was based on the methodology presented in the already mentioned report [Kushch, Smirnova, 2007]. This study was conducted in two stages: conducting a survey of experts to identify the preferences of industrial companies in terms of the roles of participants in digital platforms in the development of their interaction; processing the information received from the results of the survey. Let's consider each stage of the study in more detail.
At the first stage, a survey of 91 industrial companies was conducted (Table 8). In the questionnaires, it was proposed to determine the role of each participant in the development of interaction between instrumental, infrastructure and applied digital platforms. As the roles of participants in digital platforms, the areas of activity of each participant were indicated, described in Tables 5-7.
At the second stage of the study, the information obtained during the survey of experts was processed. The results of the study are presented in Fig. 5-7.
Thus, the development of relationships between the participants of the instrumental digital platform is influenced by the integration of all participants in the implementation of the following roles:
- high level of productivity;
- ensuring the efficiency of the digital platform;
- ensuring the creation of a single technological platform;
- bid data storage and processing;
- forming a resource strategy.
Thus, the development of relationships between participants on the infrastructure digital platform is influenced by the integration of all participants in the implementation of the following roles:
- ensuring the efficiency of the digital platform;
- high level of productivity;
- ensuring the creation of a single technological platform;
- communication management with the developer of the infrastructural digital platform;
- use of related IT services and digital platforms.
Thus, the development of relationships between participants on the applied digital platform is influenced by the integration of all participants in the implementation of the following roles:
- ensuring the functioning of business processes of the digital platform for developers of IT services;
- sale of goods and services;
- request for goods and services provided within the applied digital platform;
- provision of all necessary information about goods and services;
- management of communications with owners of information sources.
Table 2
Customer relationship management strategies
|
Strategy |
Characteristic |
|
Market segmentation |
Formation of different groups (segments) to better meet the needs of business consumers [Sen, Sinha, 2011] |
|
Choice of business consumers |
Business consumers can choose within three strategies [Understanding business markets.., 1990]: • focusing on a particular market; • definition of benefits provided for each segment; • the ratio of values for the client and the level of costs |
|
Building a portfolio of relationships |
Preference is given to long-term strategic relationships with partners. In some cases, building short-term partnerships is possible [Hilton et al., 2020] |
Source: compiled by the author according to [Understanding business markets.., 1990; Sen, Sinha, 2011; Hilton et al., 2020].
Table 1
Supplier relationship management strategies
|
Strategy |
Characteristic |
|
Purchasing strategy development |
This strategy assumes the centralisation of procurement, the development of procurement strategies for each product group, the formation of procurement quality strategies, the annual adjustment of the procurement strategy [Kushch, Smirnova, 2007; Shiralkar et al., 2022] |
|
Supplier selection |
Supplier selection and evaluation should include several steps [Urazova, 2009]: 1. Analysis of the range of purchased products 2. Determining the role of the supplier in the production processes 3. Determining the criteria for a good supplier in different categories 4. Supplier portfolio analysis and evaluation 5. Implementation of work with the supplier |
|
Supplier development |
The development of suppliers should be carried out primarily in two directions [Kushch, Smirnova, 2007]: • development aimed at strengthening the system of common values and goals with the supplier; • technological development |
|
Communication process management |
The formation of a strategy for communication processes with a supplier should be carried out at the level of the company's top management and take into account short-term and long-term relationships with the supplier. In modern conditions of high uncertainty and turbulence, it is preferable to build strategic (long-term) relationships with the supplier [Kushch, Smirnova, 2007] |
|
Cost management |
Cost management should include many aspects: supplier relationship management in terms of profitability, technology management, etc. [Kim, Choi, 2021] |
|
Logistics management |
Supply chain management can be carried out within various concepts - JIT, Kanban, etc. [Kim, Choi, 2021] |
|
Monitoring |
Supplier relationships should be continuously monitored [Kim, Choi, 2021] |
Source: compiled by the author after [Kushch, Smirnova, 2007; Urazova, 2009; Kim, Choi, 2021; Shiralkar et al., 2022].
Table 3
Integrated models of relationship management between partner companies
|
Model |
Characteristic |
|
CPFR (Collaborative Planning, Forecasting and Replenishment) |
Management of intercompany interactions through strict regulation and sequence of execution of all business processes. At the same time, forecasting and planning of business processes is carried out jointly between partners [Hill et al., 2018; Reusen, Stouthuysen, 2020] |
|
JIT (Just in Time) |
A logistics concept that allows just-in-time deliveries to be shared by all partners [Chen, Bidanda, 2019; Goyal et al., 2020] |
|
TQM (Total Quality Management) |
The concept of total quality management, which is aimed at improving the quality of all organisational processes of partners [Goyal et al., 2019; Wei et al., 2020] |
|
LP (Lean Production) |
The concept of lean production, which is aimed at eliminating waste of resources at all levels of production and involves production partners in this process [Rossini et al., 2019] |
Source: compiled by the author after [Hill et al., 2018; Chen, Bidanda, 2019; Goyal et al., 2019; Rossini et al., 2019; Goyal et al., 2020; Reusen, Stouthuysen, 2020; Wei et al., 2020].
Table 4
Types of digital platforms
|
Type |
Characteristics |
|
Instrumental digital platform |
It is based on a software or hardware-software complex (product) designed to create software or hardware-software solutions for applied purposes. Examples: Java, iOS, Microsoft Azure, Intel, SAP.HANA, etc. |
|
Infrastructure digital platform |
It is based on an ecosystem of participants in the informatisation market, the purpose of which is to accelerate the launch to the market and provide consumers in sectors of the economy with solutions to automate their activities (IT services) using end-to-end digital technologies for working with data and access to data sources implemented in the infrastructure of this ecosystems. Examples: PREDIX, ArcGIS, CoBrain, Era Glonass, Public Services, etc. |
|
Applied digital platform |
A business model for providing the possibility of an algorithmic exchange of certain values between a significant number of independent market participants by conducting transactions in a single information environment, leading to a reduction in transaction costs through the use of digital technologies and changes in the division of labor system. Examples: Yandex.Taxi, Avito, avasales, Plato, Booking.com, Uber, etc. |
|
Industry digital platform |
It includes participants in business processes of specific industries: manufacturing, trading and service companies, their customers, as well as government regulatory services. In technological terms, industry digital platforms are information systems for accumulating, exchanging and managing data in a structured form, as well as for calling business functions with information systems of platform participants connected to it through technological interfaces. |
Source: compiled by the author based on [Digital Platforms.., 2018; Digital platforms, 2022].
Table 5
Mechanism of interaction of participants of the instrumental digital platform
|
Participants of instrumental digital platform |
Mechanism of interaction / activities |
|
Platform developers |
• Ensuring the creation of a single technological platform: it is planned to create a single set of technologies, a single digital platform architecture, ensure the integration of the digital platform roadmap and the integration of digital platform components • Ensuring the creation of a single functional scope: the creation and formation of transactional components, analytical components, industry components • Formation of product history: it is planned to form a long-term strategy for the development of the company, the formation of detailed documentation, ensuring the functioning of the technical support service • High level of performance: providing support for horisontal and vertical clustering, generating metrics for internal testing of the digital platform • Ensuring the effectiveness of the digital platform functioning: effective implementation of the digital platform in the activities of an industrial company, attracting consumers and customers to the company, ensuring high rating positions of industrial companies |
|
Solution developers |
• Formation of solutions for instrumental digital platforms: development of business strategies, formation of the architecture of technical solutions, provision of technical support for business processes and digital products, implementation of end-to-end technologies, implementation of industry 4.0 technologies, ensuring IT infrastructure flexibility • Determining the needs of software product users, software and hardware solutions: conducting market research, market segmentation, building a portfolio of relationships, managing communication processes, training and developing users, ensuring continuous monitoring of relationships between participants in the instrumental digital platform • Forming a resource strategy: attracting resources for the smooth implementation of the company's business activities; ensuring sustainable competitive advantages through the formation and implementation of the resource strategy of an industrial company |
|
Users |
• Forming a large amount of data in an instrumental digital platform: this direction involves the formation of a large pool of information for subsequent storage, aggregation and use of data for making management decisions • Storage and processing of a large amount of data: software and hardware solutions of the instrumental digital platform are aimed at implementing the storage and processing of the entire pool of information contained in the digital platform • Making managerial decisions based on the processing of a large amount of data: within the framework of this direction, it is supposed to make managerial decisions and form strategies for an industrial company |
Source: compiled by the author after [Kushch, Smirnova, 2007; Galagan, 2019; Digital marketplace.., 2022; Ratten, 2022; Xie et al., 2022].
Fig. 1. Coordination of the relationship management processes of the participants of the instrumental digital platform
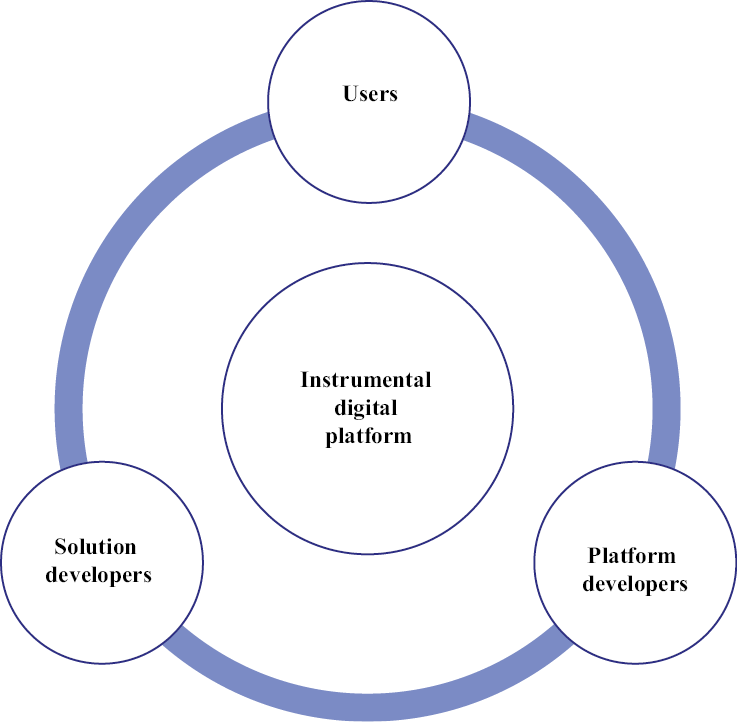
Source: compiled by the author according to [Digital Platforms.., 2018; Galagan, 2019; Ratten, 2022; Xie et al., 2022].
Table 6
Mechanism of interaction of participants of the infrastructure digital platform
|
Participants of the infrastructure digital platform |
Mechanism of interaction / directions |
|
Information supplier |
Ensuring the provision of information services for individuals and legal entities Provision of services for individuals and legal entities |
|
Platform operator |
Management of communications with owners of information sources Data warehouse management of the digital platform Ensuring the functioning of business processes of a digital platform for developers of IT services Management of communications with the developer of infrastructure digital platform |
|
Platform developer |
Ensuring the creation of a single technology platform: it is planned to create a single set of technologies, a single digital platform architecture, ensure the integration of the digital platform roadmap and the integration of digital platform components Ensuring the creation of a single functional coverage: the creation and formation of transactional components, analytical components, industry components Formation of product history: it is planned to form a long-term strategy for the development of the company, the formation of detailed documentation, ensuring the functioning of the technical support service High level of performance: providing support for horisontal and vertical clustering, generating metrics for internal testing of the digital platform Ensuring the effectiveness of the functioning of the digital platform: effective implementation of the digital platform in the activities of an industrial company, attracting consumers and customers to the company, ensuring high rating positions for industrial companies |
|
IT service developers |
Development of IT services to ensure the effective functioning of digital platforms Ensuring integration and consistency |
|
IT service users |
Request for services provided within the applied digital platform Receiving services provided within the infrastructure digital platform Use of related IT services and digital platforms |
Source: compiled by the author according to [Digital Platforms.., 2018; Galagan, 2019; Wagner et al., 2021; Choosing a Transformational Solution, 2022; Liu et al., 2022; Approaches to the definition.., no date].
Fig. 2. Coordination of the processes of managing the relationships of the participants of the infrastructure digital platform
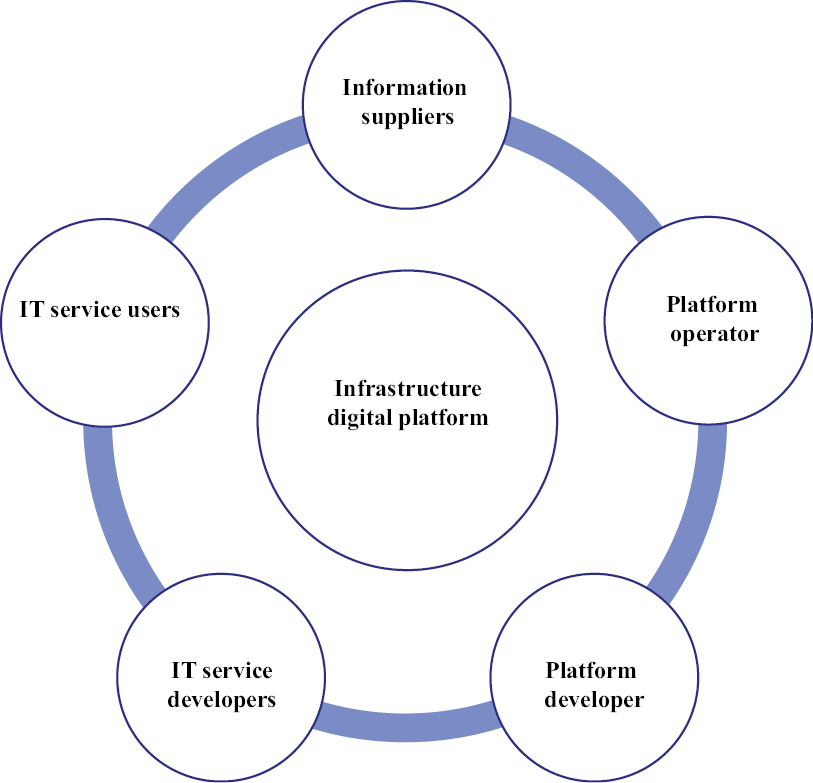
Source: compiled by the author according to [Digital platforms.., 2018; Galagan, 2019; Wagner et al., 2021; Liu et al., 2022].
Table 7
Mechanism of interaction of participants of the applied digital platform
|
Participants of the applied digital platform |
Mechanism of interaction/directions |
|
Suppliers of goods and services |
Providing all necessary information about goods and services Sale of goods and services |
|
Platform operator |
Management of communications with owners of information sources Data warehouse management of the digital platform Ensuring the functioning of business processes of a digital platform for developers of IT services Managing communications with the developer of the applied digital platform |
|
Consumers |
Request for goods and services provided within the applied digital platform Purchase of goods and services provided within the application platform Use of related IT services and digital platforms |
|
Regulators |
Ensuring legal requirements Implementation of monitoring and regulation of economic activity |
Source: compiled by the author according to [Stecken et al., 2019; Cozzolino et al., 2021; Approaches to the definition.., no date.].
Fig. 3. Coordination of the relationship management processes of the participants of the applied digital platform
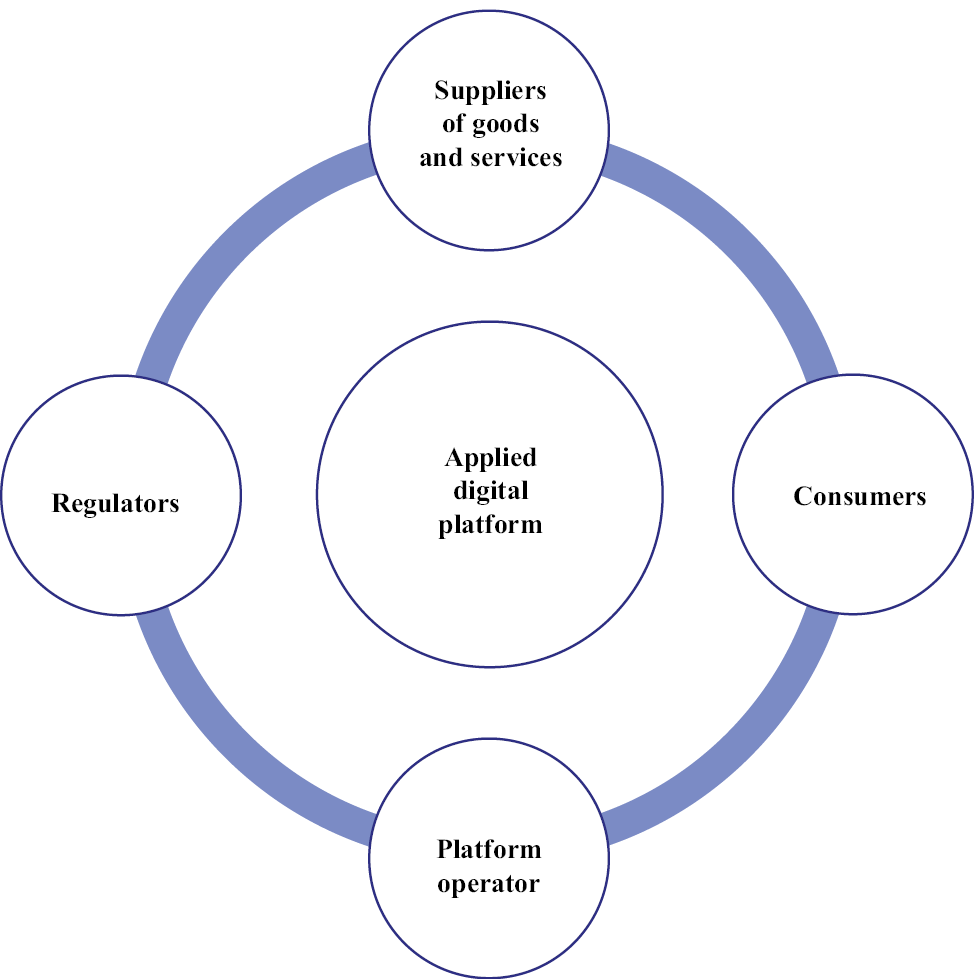
Source: compiled by the author according to [Digital Platforms.., 2018; Stecken et al., 2019; Cozzolino et al., 2021].
Table 8
Description of the sample of industrial companies participating in the study
|
Industry |
Number of companies in the sample |
Share of companies in the sample (%) |
|
Mining |
10 |
11 |
|
Production of consumer goods |
18 |
20 |
|
Chemical production |
14 |
15 |
|
Manufacture of machinery and equipment, including electrical equipment |
9 |
10 |
|
Cosmetic and pharmaceutical industry |
19 |
21 |
|
Other |
21 |
23 |
Source: compiled by the author.
Fig. 4. Levels of relationships between participants of digital platforms
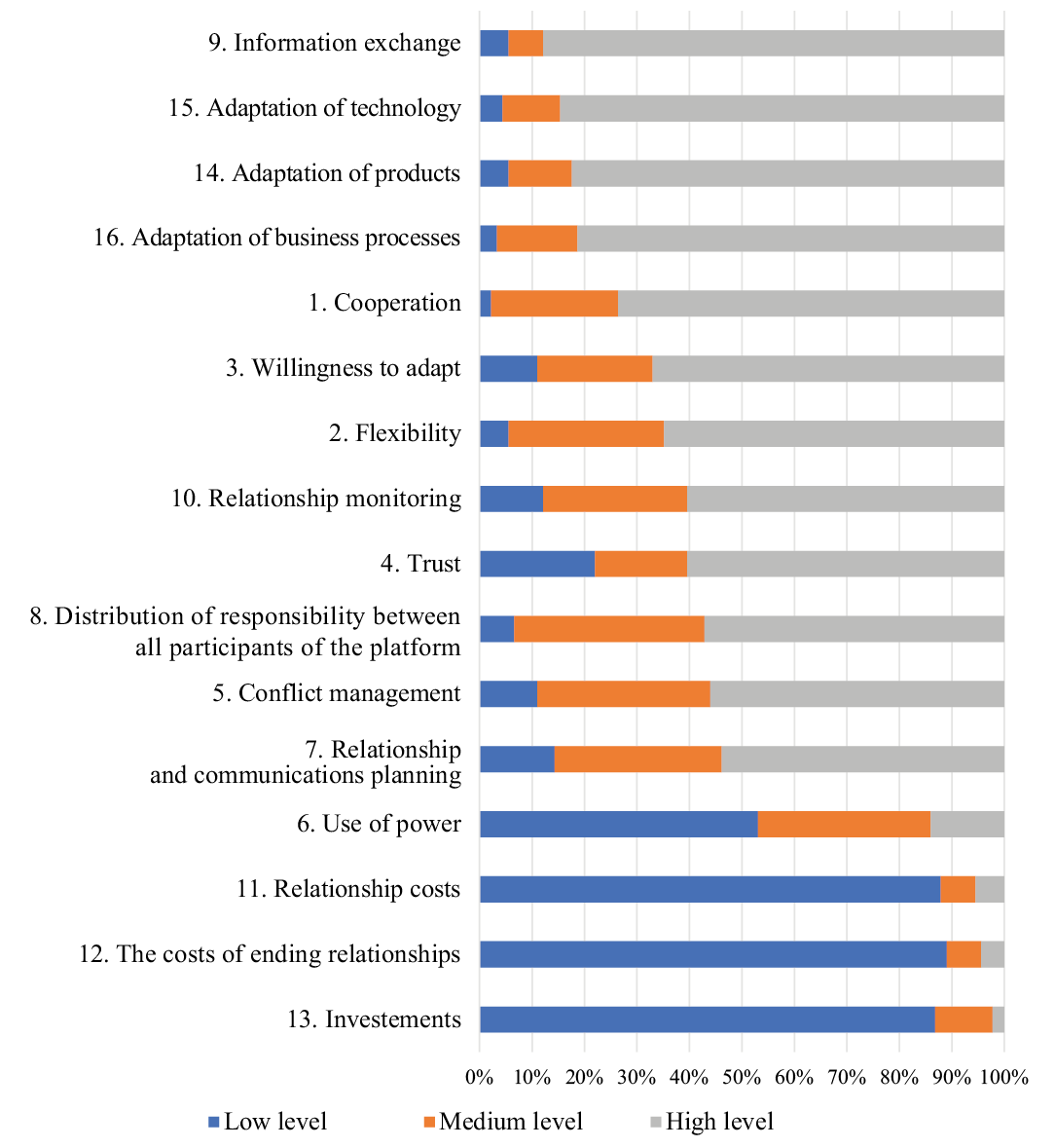
Source: compiled by the author.
Table 9
The main directions of the mechanism of interaction of participants of digital platforms
|
Mechanism line |
Line aspects |
|
Social |
1. Cooperation 2. Flexibility 3. Willingness to adapt 4. Trust 5. Conflict management 6. Use of power |
|
Managerial |
7. Relationship and communication planning 8. Distribution of responsibility between all participants of the digital platform 9. Information exchange 10. Relationship monitoring |
|
Economic |
11. Relationship Costs 12. Costs of termination of relationship 13. Investments |
|
Technological |
14. Product customisation 15. Technology adaptation 16. Adaptation of business processes |
Source: compiled by the author according to [Kushch, Smirnova, 2007; Silva et al., 2021].
Fig. 5. The role of the participants of the instrumental digital platform in the development of their relationships
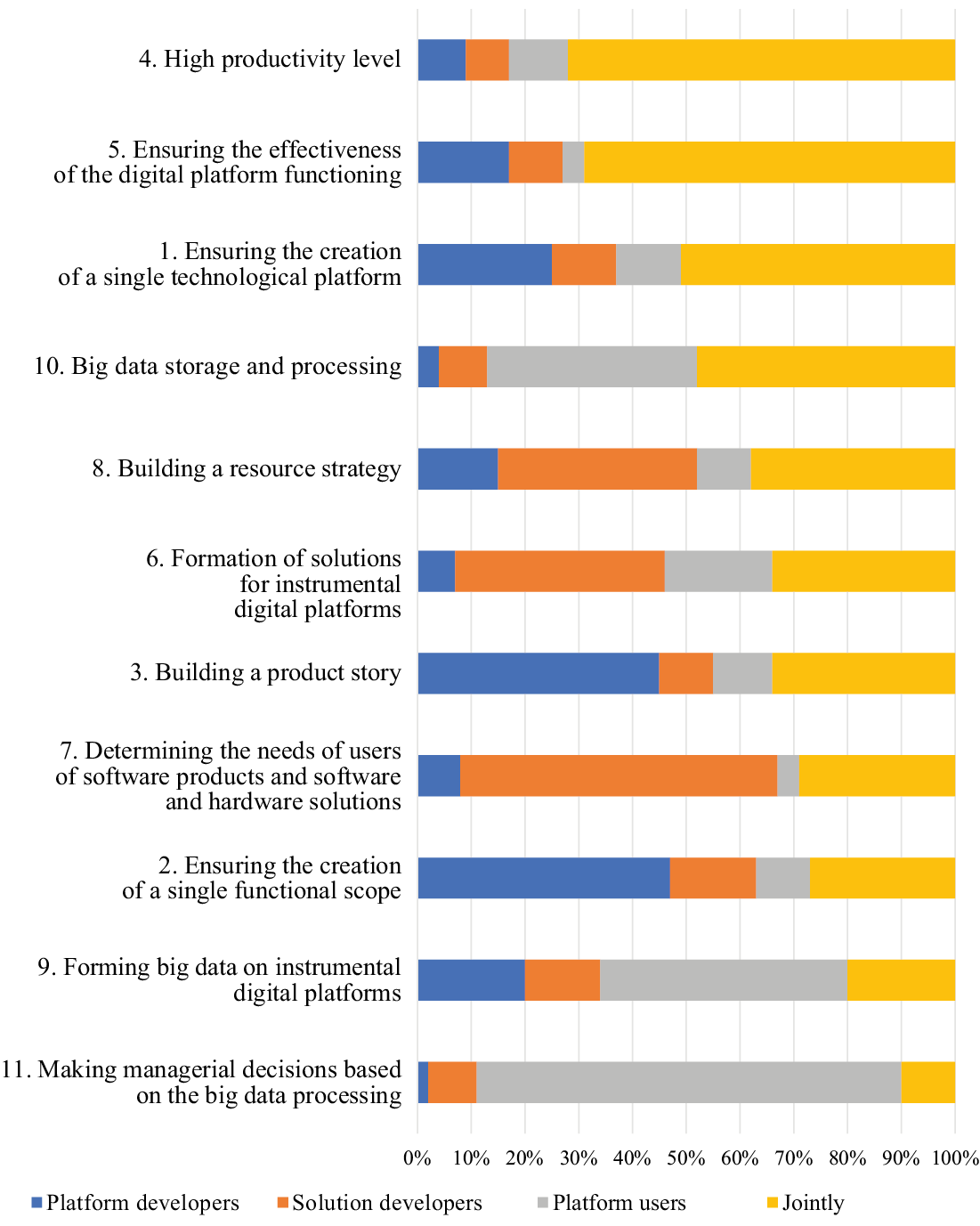
Source: compiled by the author.
Fig. 6. The role of the participants of the infrastructure digital platform in the development of their relationships (% of respondents)
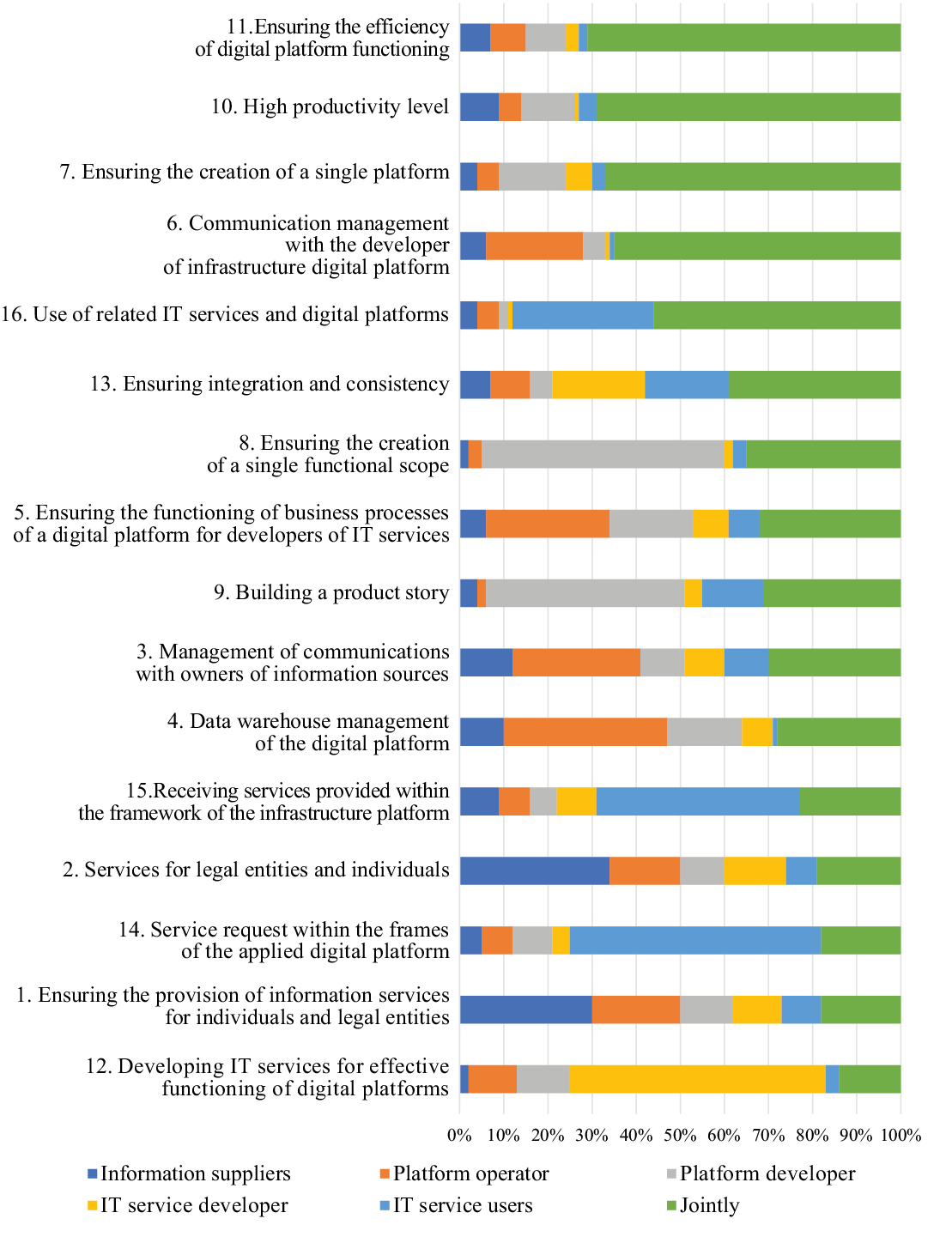
Source: compiled by the author.
Fig. 7. The role of the participants of the applied digital platform in the development of their relationships
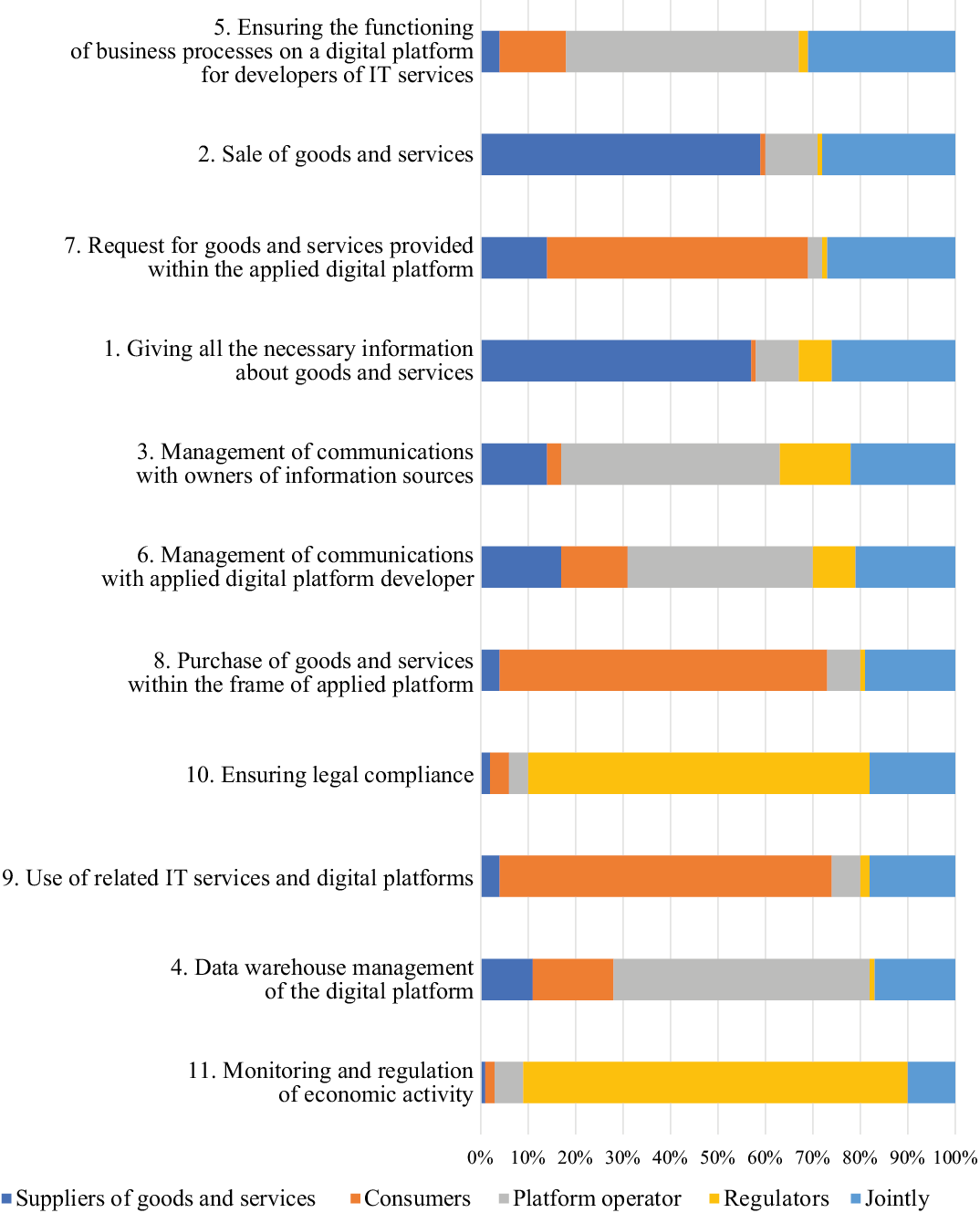
Source: compiled by the author.
-
Conclusions and results
The article considers the features of the mechanisms on digital platforms of instrumental, infrastructure and applied types. Instrumental digital platforms allow to reduce the cost of developing software and hardware-software solutions. Infrastructural and applied digital platforms are aimed at reducing transaction costs. The work of instrumental digital platforms is based on the interaction of three groups of participants: platform developers, solution developers and users. The functioning of infrastructure digital platforms is based on the interaction of five groups of participants: platform developers, platform operator, information providers, users of IT services, developers of IT services. The work of applied digital platforms is based on the interaction of four groups of participants: suppliers of goods and services, the platform operator, consumers, and regulators. The proposed mechanisms for building digital platforms are aimed at:
- ensuring the integration of services, technologies and participants of digital platforms;
- reduction of transaction costs and increase of competitiveness;
- ensuring the efficiency of the digital platform.
In this work, a study was conducted to identify various aspects in the relationship between participants in digital platforms, which showed that the relationship between participants in digital platforms is at a high level in four areas: social, managerial, economic and technological. This was confirmed based on a survey of experts.
The author also conducted a study to determine the role of each participant in the development of their relationships within digital platforms of instrumental, infrastructure and applied types. Based on the results of participants’ roles study on the instrumental digital platform, it was revealed that for the development of their relationship it is important to ensure the integration of participants in the following areas: high level of productivity, ensuring the effectiveness of the functioning of the digital platform, ensuring the creation of a single technological platform, storage and processing of large amounts of data, formation of a resource strategy. According to the results of participants’ roles study on the infrastructure digital platform, for the development of their relationship, it is important to ensure the integration of participants in the following areas: ensuring the effectiveness of the digital platform functioning, high level of performance, ensuring the creation of a single technological platform; managing communications with the developer of the infrastructure digital platform, use of related IT services and digital platforms. The results of participants’ roles study on the applied digital platform showed that in order to develop their relationship, it is important to ensure the integration of participants in the following areas: ensuring the functioning of business processes of the digital platform for developers of IT services, sale of goods and services, request for goods and services provided within the applied digital platform, providing all the necessary information about goods and services, management of communications with the owners of information sources. Thus, the development of relationships between participants on digital platforms is influenced by the integration of all participants, which provides a synergetic effect.
References
1. Choosing a transformational solution (2022). Training Center for Leaders and Digital Transformation Teams. https://strategy.cdto.ranepa.ru/6-2-cifrovye-proekty-i-platformy. (In Russ.)
2. Galagan D. (2019). Tool platforms. The core of digital transformation of authorities. IBS. https://www.tadviser.ru/images/8/83/5.%D0%93%D0%B0%D0%BB%D0%B0%D0%B3%D0%B0%D0%BD_28.05.19_19.pdf. (In Russ.)
3. Kushh S.P., Smirnova M.M. (2007). The mechanism for coordinating the processes of managing the companyʼs relationship with partners. Scientific reports 6(R). Saint Petersburg, SPbGU. https://dspace.spbu.ru/bitstream/11701/820/1/6%28R%29_2007.pdf. (In Russ.)
4. Approaches to the definition and typification of digital platforms (w.y.). https://files.data-economy.ru/digital_platforms_project.pdf. (In Russ.)
5. Urazova N. (2009). Supplier selection and evaluation. ElektroInfo journal, 1. https://www.cfin.ru/management/manufact/supplier_choice_and_evaluation.shtml. (In Russ.)
6. Digital marketplace: Catalog of the Russian software (2022). Digital platforms. https://diplatforms.ru/project/digitalmarketplace. (In Russ.)
7. Digital platforms. Approaches to definition and typification (2018). Rostelecom. https://d-russia.ru/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/digital_platforms.pdf. (In Russ.)
8. Digital platforms (2022). Competence Development Center in Business Informatics, Logistics and Project Management of the Higher School of Business. https://hsbi.hse.ru/articles/tsifrovye-platformy/. (In Russ.)
9. Chen Zh., Bidanda B. (2019). Sustainable manufacturing production-inventory decision of multiple factories with JIT logistics, component recovery and emission control. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 128: 356-383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tre.2019.06.013.
10. Cozzolino A., Corbo L., Aversa P. (2021). Digital platform-based ecosystems: The evolution of collaboration and competition between incumbent producers and entrant platforms. Journal of Business Research, 126: 385-400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2020.12.058.
11. Goyal A., Agrawal R., Saha C.R. (2019). Quality management for sustainable manufacturing: Moving from number to impact of defects. Journal of Cleaner Production, 241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118348.
12. Goyal S., Ahuja M., Kankanhalli A. (2020). Does the source of external knowledge matter? Examining the role of customer co-creation and partner sourcing in knowledge creation and innovation. Information & Management, 57(6). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.im.2020.103325.
13. Hill C.A., Zhang G.P., Miller K.E. (2018). Collaborative planning, forecasting, and replenishment & firm performance: An empirical evaluation. International Journal of Production Economics, 196: 12-23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2017.11.012.
14. Hilton B., Hajihashemi B., Henderson C.M., Palmatier R.W. (2020). Customer success management: The next evolution in customer management practice? Industrial Marketing Management, 90: 360-369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2020.08.001.
15. Kim Y., Choi T.Y. (2021). Supplier relationship strategies and outcome dualities: An empirical study of embeddedness perspective. International Journal of Production Economics, 232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2020.107930.
16. Liu Y., Wu A., Song D. (2022). Exploring the impact of cross-side network interaction on digital platforms on internationalization of manufacturing firms. Journal of International Management. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intman.2022.100954.
17. Ratten V. (2022). Digital platforms and transformational entrepreneurship during the COVID-19 crisis. International Journal of Information Management. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2022.102534
18. Reusen E., Stouthuysen K. (2020). Trust transfer and partner selection in interfirm relationships. Accounting, Organizations and Society, 81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aos.2019.101081.
19. Rohn D., Bican P.M., Brem A., Kraus S., Clauss Th. (2021). Digital platform-based business models – An exploration of critical success factors. Journal of Engineering and Technology Management, 60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jengtecman.2021.101625.
20. Rossini M., Costa F., Staudacher A.P., Tortorella G. (2019). Industry 4.0 and lean production: An empirical study. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 52(13): 42-47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifacol.2019.11.122.
21. Sen A., Sinha A.P. (2011). IT alignment strategies for customer. Decision Support Systems, 51(3): 609-619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2010.12.014.
22. Shiralkar K., Bongale A., Kumar S. (2022). Issues with decision making methods for supplier segmentation in supplier relationship management: A literature review. Materials Today: Proceedings, 50(5): 1786-1792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.09.197.
23. Silva H.D., Azevedo M., Soares A.L. (2021). A vision for a platform-based Digital-Twin ecosystem. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 54(1): 761-766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifacol.2021.08.088.
24. Stecken J., Ebel M., Bartelt M., Poeppelbuss J., Kuhlenkötter B. (2019). Digital shadow platform as an innovative business model. Procedia CIRP, 83: 204-209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2019.02.130.
25. Ford D. (ed.). Understanding business markets. Interaction, relationships and networks (1990). London, Academic Press.
26. Wagner G., Prester J., Pare G. (2021). Exploring the boundaries and processes of digital platforms for knowledge work: A review of information systems research. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 30(4). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsis.2021.101694.
27. Wei F., Feng N., Yang Sh., Zhao Q. (2020). A conceptual framework of two-stage partner selection in platform-based innovation ecosystems for servitization. Journal of Cleaner Productio, 262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121431.
28. Xie X., Han Y., Anderson A., Ribeiro-Navarrete S. (2022). Digital platforms and SMEs’ business model innovation: Exploring the mediating mechanisms of capability reconfiguration. International Journal of Information Management, 65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2022.102513.
About the Author
M. O. KuznetsovaРоссия
Candidate of economic sciences, senior research scientist of Department of Management and Innovation, Faculty «Higher School of Management», Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation (Moscow, Russia). https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4403-3800. Research interests: strategic sustainability, risk management, strategic management.
Review
For citations:
Kuznetsova M.O. FORMATION OF A STRATEGY AND MECHANISM OF INTERACTION BETWEEN PARTICIPANTS OF DIGITAL PLATFORMS. Strategic decisions and risk management. 2022;13(3):255-266. https://doi.org/10.17747/2618-947X-2022-3-255-266
JATS XML










































