Scroll to:
STRATEGIC SUSTAINABILITY OF INDUSTRIAL COMPANIES: АPPROACHES TO UNDERSTANDING AND RISK ANALYSIS
https://doi.org/10.17747/2618-947X-2020-2-196-205
Abstract
The article analyzes approaches to the strategic sustainable development of industrial organizations. Based on the review of Russian and foreign literature, three approaches to the strategic sustainable development of industrial organizations were identified: process, system and time approaches.
Based on the analysis of annual reports of Russian industrial organizations, it was possible to identify and systematize the risks that affect the strategic stability of Russian industrial organizations. Among the identified risks, the following risk groups are identified: country risks, legal risks, industry risks, foreign economic risks, market risks, production and technological risks, financial risks, reputational risks, environmental risks, information risks, social risks and strategic risks.
As a result of correlation and regression analysis, the most significant risks affecting the achievement of strategic goals of Russian industrial organizations were identified. These include: country risks, industry risks, and strategic risks. The obtained regression model allows us to predict the degree of achievement of strategic goals of Russian industrial organizations under the influence of various risks.
Keywords
For citations:
Kuznetsova M.O. STRATEGIC SUSTAINABILITY OF INDUSTRIAL COMPANIES: АPPROACHES TO UNDERSTANDING AND RISK ANALYSIS. Strategic decisions and risk management. 2020;11(2):196-205. https://doi.org/10.17747/2618-947X-2020-2-196-205
1. INTRODUCTION
Modern industrial companies operate in conditions of a high turbulence of external and internal environment, which is due to the growing level of competition, digitalization processes, and changes in the international economic and political environment. Under these conditions, domestic industrial organizations are exposed to various threats that have a significant impact on their sustainable development. Consequently, there is a need to develop new methods and approaches to ensure the sustainable development of industrial organizations. For this reason, the importance of theoretical understanding of this economic category is increasing.
2. STRATEGIC SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT AS A RESEARCH SUBJECT
Within the sustainable development approach, the concept of strategic sustainability has emerged, which assumes that an organization performance indicators do not have significant changes or are in positive dynamics for a long period of time, for instance in the works of [Grigorieva, 2013; Dudin, 2013].
The analysis of research allows us to identify the existing approaches to determining strategic sustainability which are summarized in table 1.
Table 1
The comparison of definitions of strategic sustainability
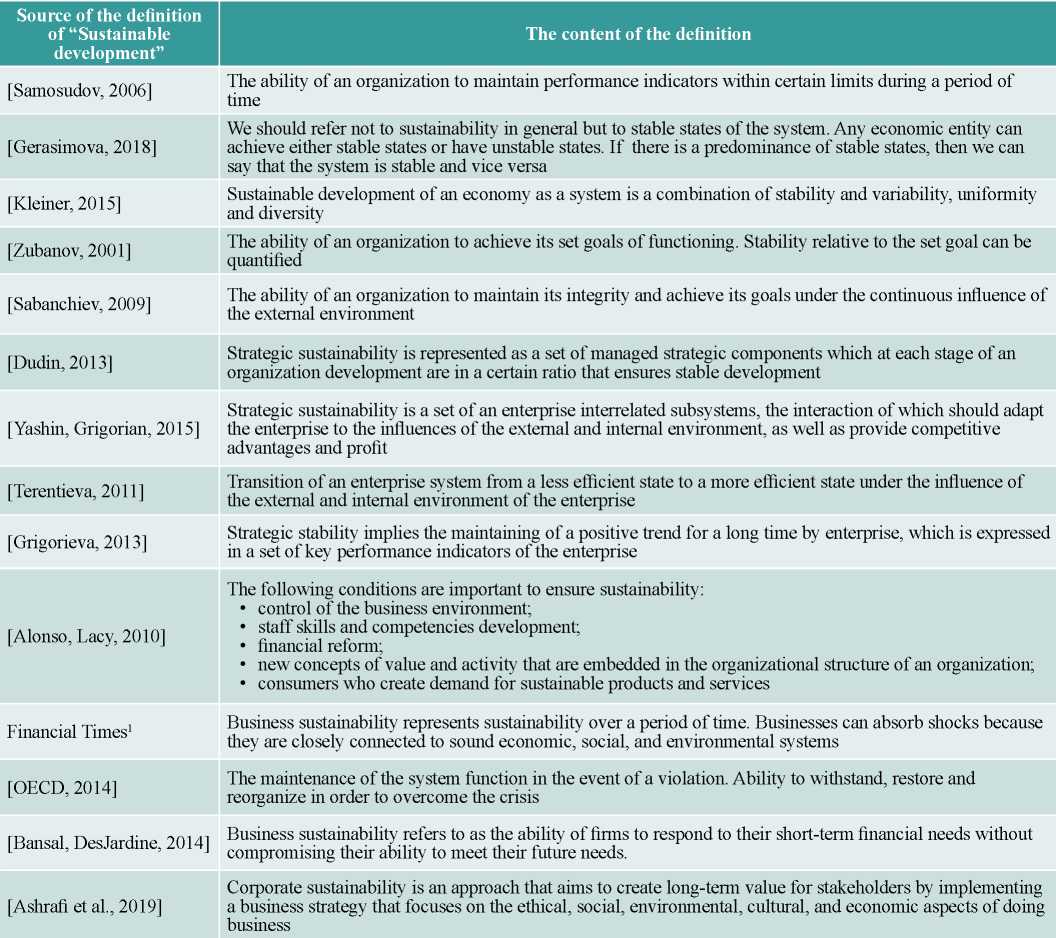
Source: compiled by the author.
The table summarizes the definitions of strategic sustainability provided by authors who are engaged in research in this area, as well as scientists who study various areas of management and economics. The analysis of the strategic sustainability definitions allows us to identify process, system, and temporal approaches to understanding this category.
Researchers who adhere to the process approach, such as Tatyana Terentieva [Terentieva, 2011], Pratima Bansal and Mark R. DesJardine [Bansal, DesJardine, 2014] believe that achieving strategic sustainability is possible by managing external and internal environmental factors.
Thus, Bansal and DesJardine describe the main objectives of strategic sustainability as:
- minimizing the impact of risk factors;
- increasing of efficiency of organizations management;
- effective management at the operational level to achieve the strategic sustainability of an organization.
As the main goal of achieving the strategic sustainability, in such works as [Sabanchiev, 2009; Alonso, 2010 Lacy; Dudin, 2013; OECD, 2014; Kleiner, 2015; Gerasimova, 2018; Ashrafi et al., 2019], proponents of the system approach consider the sustainability of the individual components of the system that will lead to sustainability in general.
Researchers in the framework of the systematic approach, have identified several tasks for achieving sustainable development:
- ensuring balanced development of various subsystems of an organization;
- ensuring the flexibility of an economic entity and all its subsystems to achieve system sustainability;
- providing a synergistic effect that will increase the stability of the business entity.
The followers of the temporal approach to sustainable development [Samosudov, 2006; Yashin, Grigorian, 2015; Grigorieva, 2013] note that one of the main goals of achieving strategic sustainability is to maintain key performance indicators within certain limits for a certain period.
Accordingly, the main objectives of strategic sustainability are considered by the proponents of the temporary approach:
- ensuring certain values of key performance indicators of an economic entity;
- reducing the probability of deviations from the specified trajectory in the direction of achieving goals.
Thus, the described approaches to achieving of strategic sustainability consider this category from different angles:
- different levels of socio-economic systems are taken into account;
- various bases for ensuring strategic sustainability are highlighted;
- the object of research is the elements of the system and their interrelationships, Intersectionality and synergistic effect;
- various criteria for determining and evaluating strategic sustainability are highlighted.
For a more complete definition of strategic sustainability it is advisable to summarize the considered approaches as it will provide a comprehensive look at the issue of sustainability, identify all factors affecting strategic stability and find optimal methods of assessment and management.
This paper proposes an integrated approach that combines existing approaches to the definition of this category, which takes into account:
- the need for a systemic view of an industrial organization, namely the search for a balance between the development of all systems and ensuring their synergistic effect;
- formation of indicators of economic activity and their threshold values that indicate the sustainability of an industrial organization.
An integrated approach will allow to determine precisely the types of sustainability of industrial organizations, methods for assessing their sustainability, and will also allow to find methods for managing the sustainability of industrial organizations and effectively manage it.
In this article, strategic sustainability is understood as the interaction of an organization's components that allows to ensure positive dynamics of performance indicators to improve the effectiveness of the organization's functioning over a long period.
Thus, sustainable development is considered from the perspective of strategic sustainability. In order to ensure the sustainable development of an industrial organization it is necessary to build a management system that will balance the activities of all components of strategic sustainability in order to minimize the impact of external and internal environmental factors, risks and threats.
3. RISKS OF STRATEGIC SUSTAINABILITY OF INDUSTRIAL ORGANIZATIONS IN VARIOUS INDUSTRIES
The paper analyzes the risks of sustainable development of a number of industrial organizations in various industries. Based on the annual reports of the selected companies, risks affecting their activities were identified; the results of the analysis are presented in table 2.
Table 2
Analysis of risks of strategic sustainable development of industrial companies in various industries
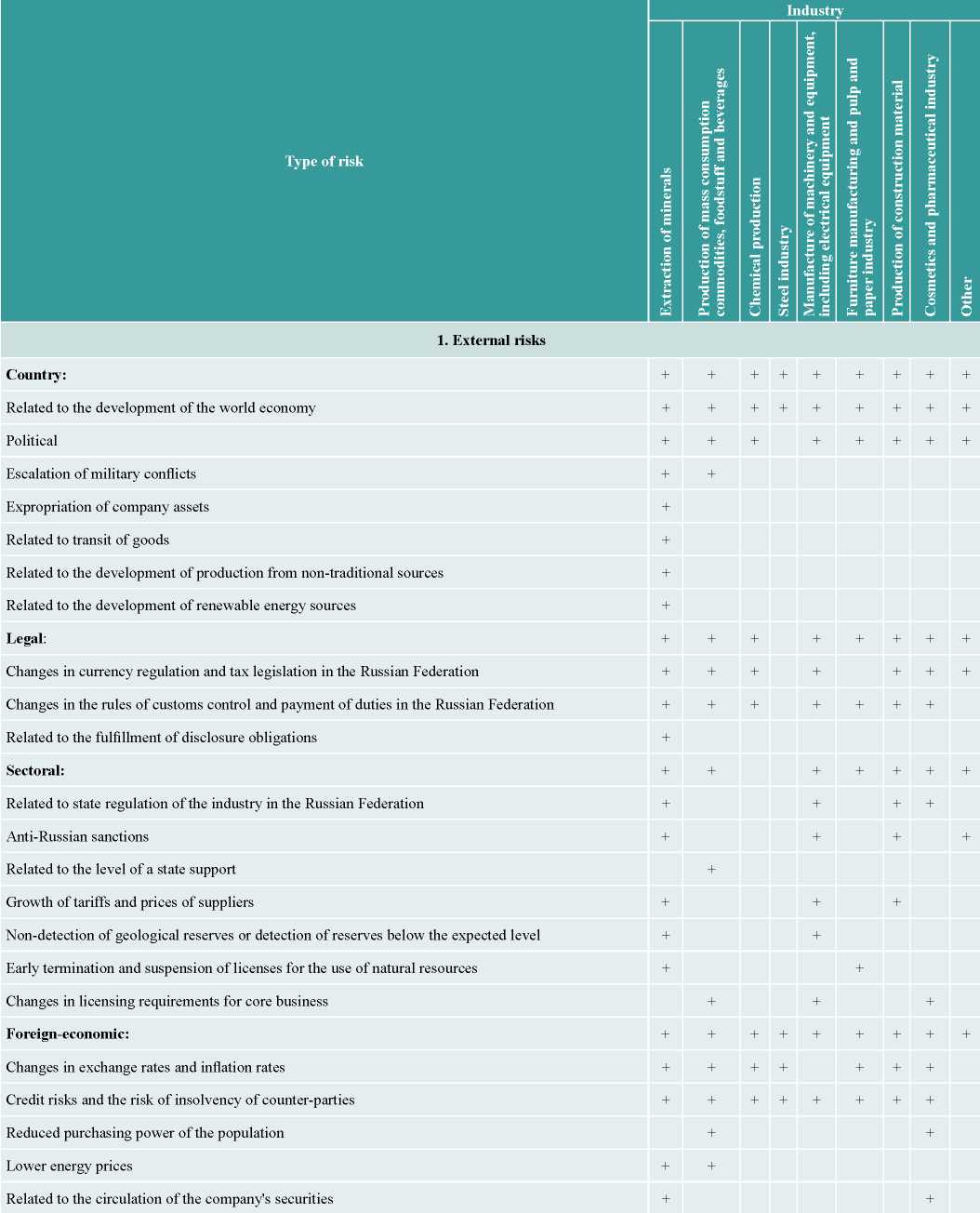
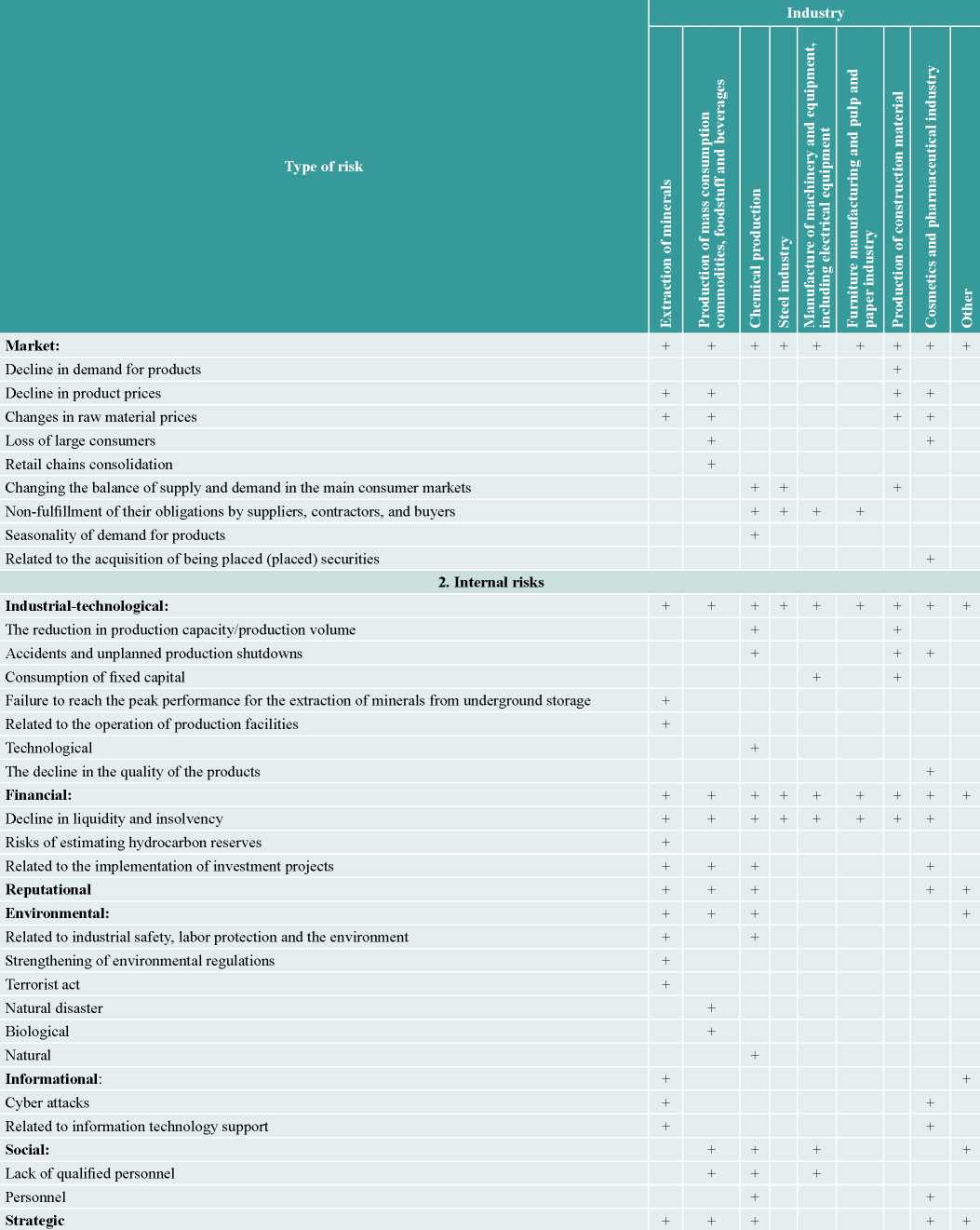
Source: compiled by the author. Based on: RBK 500. 2019 rating. URL: https://www.rbc.ru/rbc500/; Corporate Information Disclosure Center. 2019. URL: http://www.e-disclosure.ru/.
Organizations of various industries take into account the impact on sustainable development of country risks related to the development of the world economy and political. Among the country risks that are marked by exclusively mining organizations, the risks related to expropriation of assets, transit of goods, production with unconventional sources and renewable energy are highlighted too. The impact of risks related to the escalation of military conflicts was noted by organizations of the extractive industries and companies that produce mass-consumption products, food and beverages.
Industrial organizations of all industries, with the exception of metallurgical companies, take into account the impact of legal risks in their activities. Most industries note the impact of risks related to changes in currency, tax and customs regulations. Extractive industry organizations among the legal risks consider factors related to the fulfillment of obligations of disclose information.
The impact of industry risks on sustainable development is taken into account by companies of all industries, with the exception of chemical and metallurgical industries. The most common industry risks are those ones related to state regulation of industries, anti-Russian sanctions, rising of prices and tariffs and changes in licensing requirements.
Absolutely all industries take into account the impact of external economic risks on the stability of industrial organizations. The most common external economic risks include changes in exchange rates and the rate of inflation, credit risks, and factors related to the insolvency of counterparties. The impact of risks related lower energy prices was noted by mining companies and companies that produce mass-consumption products.
The impact of market risks on sustainable development is not taken into account by industrial organizations of all sectors. Among those risks only a few industries consider the following factors: lower product prices, changes in raw material prices, non-fulfillment of their obligations by suppliers, contractors, and buyers.
Industrial organizations of all sectors consider the impact of production and technological risks in their activities. In the 2018 annual reports, companies most frequently noted a decrease in production capacity/production volumes, accidents and unscheduled production stops, and consumption of fixed capital.
Also, industrial companies in all industries take into account financial risks, namely the risks of reduced liquidity and insolvency. Many industries note the risks related to the implementation of investment projects. Among the financial risks, mining companies also noted the risks related to the assessment of hydrocarbon reserves.
Based on the analysis of the risks for sustainable development of industrial organizations in various industries, it appears that modern Russian companies in their activities mainly take into account the risks related to the world economy development, political and currency risks, risks of reducing liquidity and solvency. However, not all the industries take into account market risks, such as lower demand and prices for products, changes in the balance of supply and demand in the main consumer markets, nonfulfillment of obligations by suppliers, contractors and buyers, seasonality of demand, and risks related to the acquisition of placed (being placed) securities. It should be noted that Russian industrial companies practically do not consider the impact on sustainable development of the following risk groups: reputational, environmental, informational, social and strategic.
Thus, Russian industrial companies do not take into account all the risks that have a significant impact on strategic sustainability. This is largely due to the low level of risk culture that have industrial organizations. Risk culture is understood as a system of values, beliefs and knowledge in the field of risk management that is shared and applied in practice by employees of the organization at all levels of management [Current issues of risk management, 2018]. Therefore, there is a need to improve existing risk management practices.
The study of the risks of sustainable development of industrial organizations in Russia allowed us to classify them for various industries, which is a necessary condition for developing a risk management system that will help increase the level of sustainable development of companies in various industries.
4. METHODOLOGY OF INDUSTRIAL ORGANIZATIONS RISK ANALYSIS IN VARIOUS INDUSTRIES AND THE RESEARCH RESULTS
A two-stage study was conducted to analyze the most significant risks that affect the achievement of strategic goals of industrial organizations.
The quality stage included:
1) identification of external and internal risks based on the study of annual reports of industrial organizations; formation of external and internal risk groups that affect the achievement of strategic goals of industrial organizations;
2) conducting a survey of industrial companies to determine the level of impact of risks identified at the previous stage; the representatives of 96 industrial companies in various industries were interviewed.
The quantitative stage consisted of:
1) conducting a correlation analysis of the impact of risks on the achievement of strategic goals of industrial organizations to identify a significant relationship between independent variables and dependent variables in order to select a list of risks for further analysis;
2) development of a regression model that allows to measure the degree of risk impact on the achievement of strategic goals of industrial organizations.
At the first (qualitative) stage, the entire array of risks that affect the achievement of strategic goals by industrial companies was formed (table 3), based on the study of annual reports of organizations and their further questioning.
Table 3
Factor and result indicators of regression analysis of the impact of risks on the achievement of strategic goals of industrial organizations
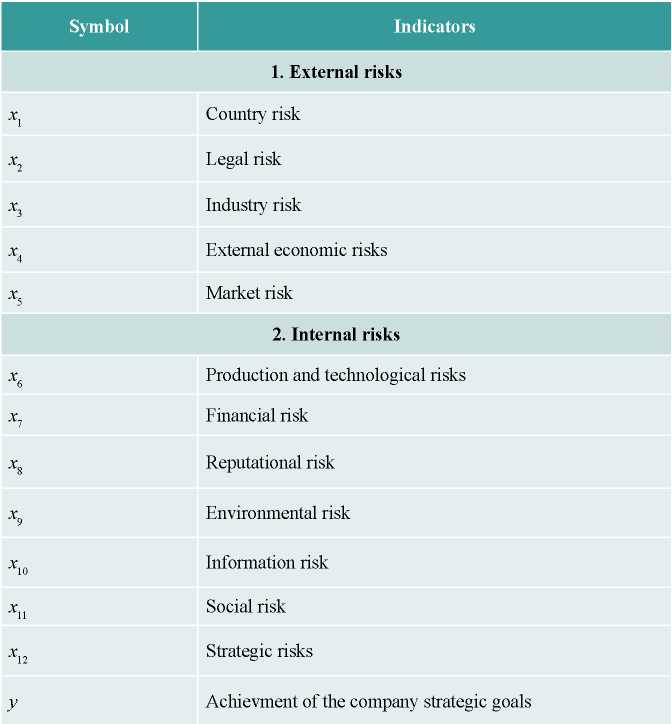
At the second (quantitative) stage, a correlation analysis of risks was performed, which made it possible to select significant risks (table 4).
Table 4
Matrix of correlation analysis of the impact of risks on the achievement of strategic goals of industrial organizations
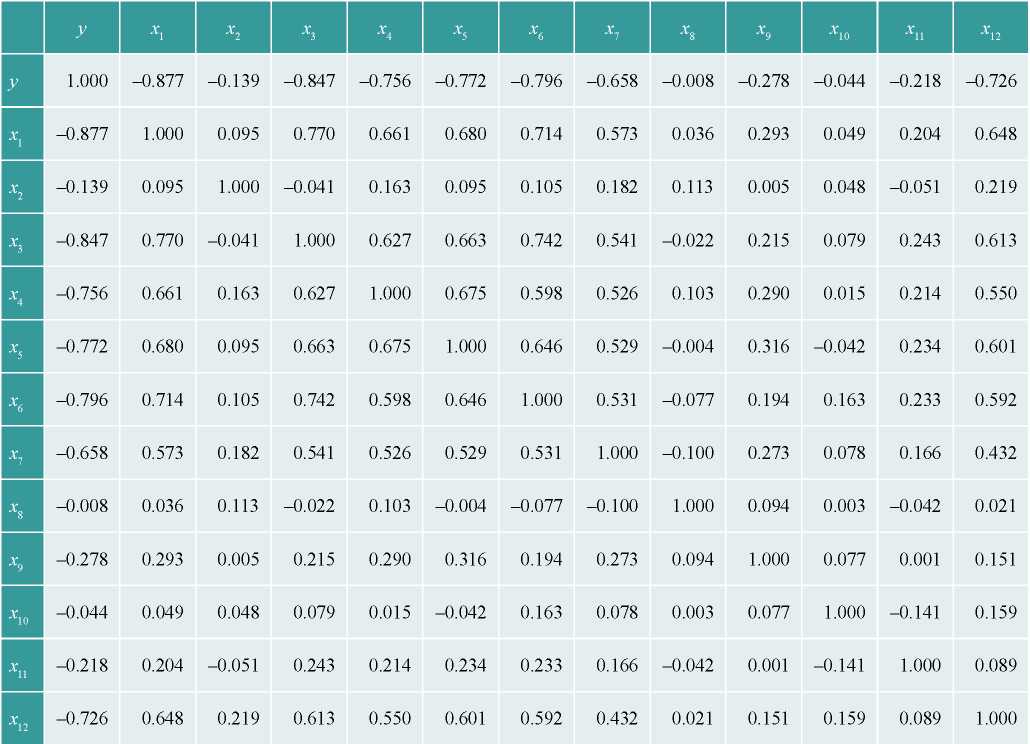
Source: compiled by the author
Based on the results of the correlation analysis, the following factors were selected: country risks (x1), industry risks (x3), foreign economic risks (x4), market risks (x5), production and technological risks (x6), financial risks (x7) and strategic risks (x12). For these factors, there is a high correlation with the dependent variable, as well as a low indicator of multicollinearity (< 0,8) of independent variables.
Then we analyzed the impact of internal and external risks on the achievement of strategic goals of industrial organizations using a regression model:
y = β0+ β1x1+ β3x3+ β4x4+ β5x5+ β6x6+ β7x7+ β12x12, (1)
where y is a dependent variable (achievement of the company's strategic goals), βI is a non-standardized coefficient, and xi is independent variables (risks).
The results of the multiple regression analysis are presented in table 5.
Table 5
The impact of external and internal risks on achievement of strategic goals of industrial organizations
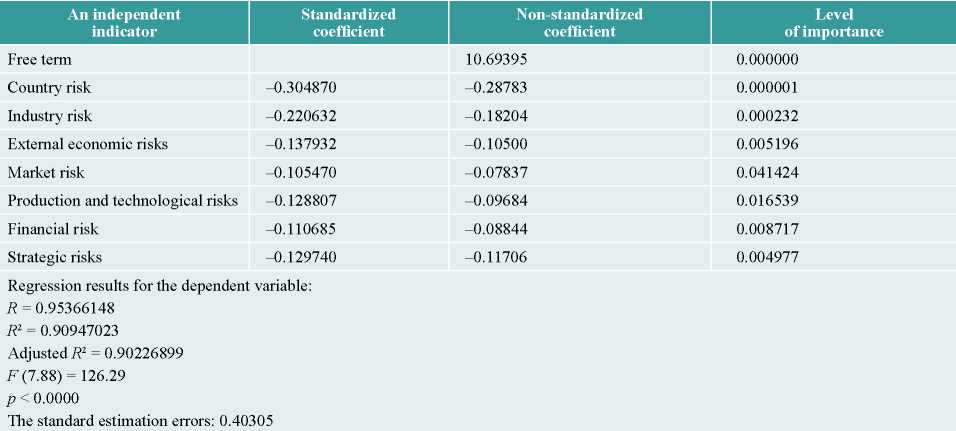
Source: compiled by the author.
The regression model showed that all the risks negatively affect the achievement of strategic goals of industrial organizations. Based on the results of calculations, the following risks were the most significant for achieving the company's strategic goals: country (β = –0.28783), industry (β = –0.18204) and strategic (β = – 0.11706). Thus, the regression model of the risks impact on the achievement of strategic goals of industrial organizations takes the following form:
Y = 10,694 - 0,288х1 - 0,182х3 - 0,105х4 - 0,078х5 - 0,097х6 - 0,088х7 - 0,117х12 (2)
Thus, the results of the correlation and regression analysis revealed three groups of risks that have the greatest impact on the strategic stability of industrial organizations. Country risks may be related to the world economy development, political risks, military conflicts, the imposition of economic sanctions, the transit of products, etc.
Industry risks are related to the specifics of state regulation of the industry, the level of state support for specific industries, tariffs and prices growth, and changes in licensing requirements for core activities.
Strategic risks are related to the choice of strategy, its implementation, and management decisions on the company development strategies.
The identified risks require special control, assessment and management, as they can cause significant damage to the strategic sustainability of an industrial organization.
The suggested regression model allows to predict the degree of achievement of strategic goals of industrial organizations under the influence of various risks, which makes it possible to manage risks and threats that can destroy strategic sustainability in a timely manner.
5. CONCLUSIONS AND PRACTICAL APPLICATION OF THE RESEARCH RESULTS
The paper considers the following aspects related to the concept of strategic sustainability.
1. Process, system, and temporal approaches to strategic stability of industrial organizations have been identified and described. In this study, strategic sustainability is viewed in terms of generalizing the suggested approaches, since this allows to provide a comprehensive view of the problem of sustainability, identify all factors that affect strategic sustainability, and select the best methods of their evaluation and management.
2. We have identified and classified the risks of the Russian industrial organizations, which influence their strategic sustainability. It was noted that domestic companies do not fully take into account the following groups of risks in their activities: reduced demand and prices for products, changes in raw material prices, changes in the balance of supply and demand in the main consumer markets, non-fulfillment of obligations by suppliers, contractors and buyers, seasonality of demand, risks related to the acquisition of placed (being placed) securities, as well as: reputational, environmental, information, social and strategic risks. In other words, Russian industrial companies do not take into account all the risks that have a significant impact on strategic sustainability, which is largely due to the low level of their risk culture.
3. Based on the correlation and regression analysis, the most significant risks that affect the strategic sustainability of Russian industrial organizations were identified. These include country, industry, and strategic risks.
The results of the study have high practical significance, as they allow:
- to view strategic sustainability from different angles, which is necessary for the optimal choice of methods for assessing and managing strategic sustainability;
- to identify strategic sustainability risks both for industrial organizations and for various industries, which is a prerequisite for successful risk management of companies, taking into account the specifics of their activities;
- to measure the degree of risk impact on the achievement of strategic goals of industrial organizations using a regression model;
- to predict the level of achievement of strategic goals of industrial organizations under the influence of various risks.
The results of the study make it necessary to develop mechanisms of managing risks and threats to strategic sustainability, which are promising areas for further research.
References
1. Aktual’nye voprosy risk-menedzhmenta [Actual issues of risk management] (2018). PWC. URL: https://www.pwc.ru / ru / riskassurance / assets / risk-management-and-compliance / e-ver-spravochnik-risk-man-july-18.pdf.
2. Gerasimova E.B. (2018). Standartizirovannyy podkhod k analizu ustoychivosti deyatel’nosti organizatsii [A standardized approach to the analysis of the sustainability of the organization]. Uchet. Analiz. Audit [Accounting. Analysis. Audit], 2, 44‑51.
3. Grigoreva S.V. (2013). Otsenka strategicheskoy ustoychivosti v razvitii predpriyatiya [Assessment of strategic sustainability in enterprise development]. Voprosy ekonomiki i prava [Issues of Economics and Law], 3, 33‑37.
4. Dudin M.N. (2013). Obespechenie strategicheskoy ustoychivosti predprinimatel’skikh struktur v usloviyakh innovatsionnogo razvitiya: Avtoref. dis. … d-ra ekon. nauk [Ensuring the strategic sustainability of business structures in the context of innovative development. Abstr. of diss. … Dr. of Econ. Sci.]. Moscow.
5. Zubanov N.V. (2001). Analiz ustoychivosti otnositel’no postavlennoy tseli kak odin iz podkhodov k opisaniyu funktsionirovaniya organizatsii v usloviyakh neopredelennosti [Analysis of sustainability relative to the goal as one of the approaches to the description of the functioning of the organization in the face of uncertainty]. Administrativno-upravlencheskiу portal [Administrative and Аdministrative Рortal]. URL: http://www.aup.ru / books / m66 / 5.htm.
6. Kleyner G.B. (2015). Ustoуchivost’ rossiyskoy ekonomiki v zerkale sistemnoy ekonomicheskoy teorii [The stability of the Russian economy in the mirror of systemic economic theory]. Voprosy ekonomiki, 12, 107‑123.
7. Sabanchiev N.A. (2009). Teoretiko-metodicheskie osnovy organizatsionnogo obespecheniya strategicheskoy ustoychivosti: Avtorefer. dis. … kand. еkon. nauk [Theoretical and methodological foundations of organizational support of strategic stability: Abstr. of diss. … Сand. of Еcon. Sci.]. Moscow.
8. Samosudov M.V. (2006). Korporativnoe upravlenie: Teoriya korporativnogo vzaimodeуstviya. Modul’naya seriya “Ekonomist-mezhdunarodnik” [Corporate governance: Theory of corporate engagement. Modular series ”International economist”]. Vserossiyskaya akademiya vneshney torgovli Minekonomrazvitiya Rossii [Russian Foreign Trade Academy of the Ministry for the Economic Development of the Russian Federation], 330.
9. Terenteva T.V. (2011). Metodologicheskie osnovy obespecheniya ustoуchivosti razvitiya rybokhozyaystvennykh predprinimatel’skikh struktur: Diss. … d-ra ekon. nauk [Methodological foundations of ensuring sustainable development of fisheries business enterprises: Diss. … Dr. of Econ. Sci.]. Vladivostok.
10. Yashin N.S., Grigoryan E.S. (2015). Metodologiya strategicheskoy ustoychivosti predpriyatiya [Methodology of strategic sustainability of an enterprise]. Vestnik SSEU REU im. Plekhanova [Bulletin of Saratov Socio-Economic Institute of Plekhanov Russian University of Economics]. URL: https://cyberleninka.ru / article / n / metodologiya-strategicheskoy-ustoychivosti-predpriyatiya / viewer.
11. Alonso M., Lacy P. (2010). A new era of sustainability. UN global compact-accenture CEO study 2010. Accenture. URL: http://www.accenture.com / SiteCollectionDocuments / PDF / Accenture_A_New_Era_of_Sustainability_CEO_Study.pdf.
12. Ashrafi М., Acciaro М., Walker T.R., Magnan G.M., Adams M. (2019). Corporate sustainability in Canadian and US maritime ports. Journal of Cleaner Production, 220, 386‑397. URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com / science / article / pii / S0959652619304871#!.
13. OECD (2014). Boosting Resilience through Innovative Risk Governance. OECD Publishing. URL: http://dx.doi.org / 10.1787 / 9789264209114‑en.
14. Bansal P., DesJardine M.R. (2014). Business sustainability: It is about time. URL: https://journals.sagepub.com / doi / full / 10.1177 / 1476127013520265.
About the Author
M. O. KuznetsovaRussian Federation
Postgraduate student, аssistant of the Department of Management, Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation. Research interests: strategic sustainability, risk management, strategic management.
Review
For citations:
Kuznetsova M.O. STRATEGIC SUSTAINABILITY OF INDUSTRIAL COMPANIES: АPPROACHES TO UNDERSTANDING AND RISK ANALYSIS. Strategic decisions and risk management. 2020;11(2):196-205. https://doi.org/10.17747/2618-947X-2020-2-196-205









































